연구
Research
임상뇌과학연구부
Division of Clinical Neuroscience
뇌혈관질환연구센터 (Research Center for Cerebrovascular Diseases)
이 영배 교수, Prof. Yeong Bae LEE
초고자장 7T MRI 를 이용하면 높은 신호대잡음비 (SNR) 의 영상을 획득할 수 있게 됨에 따라, 고해상도의 해부학적 영상을 획득할 수 있는
가능성을 열게 되었다. 초고해상도 해부학 영상을 통하여 질병의 진행에 따른 뇌 조직의 미세한 변화를 사전에 관측할 수 있게 되었고,
뇌 피질층을 구별하여 세포들의 분포를 구별할 수 있는 능력을 갖추게 되었다. 또한, 미세 혈관 영상을 통해 미세 뇌혈류 영역을 정밀한
뇌 해부학적 위치로 매칭시킬 수 있게 되었다.
Anatomical brain images of super-high resolution can obtained by using ultra-high magnetic 7.0T MRI which gives images of high signal-to-noise
ratio (SNR). Brain images of super-high resolution allow us to observe minute changes of brain tissue as brain diseases progress and
to be able to distinguish the cerebral cortex layers and cells. Also , images of minute and fine vessels have made it possible to match the
blood flow area and its anatomical region.
1
7T MRI 새로운 신경 해부학 시대를 열다 (7T MRI opens a new era of neuroanatomy)
-
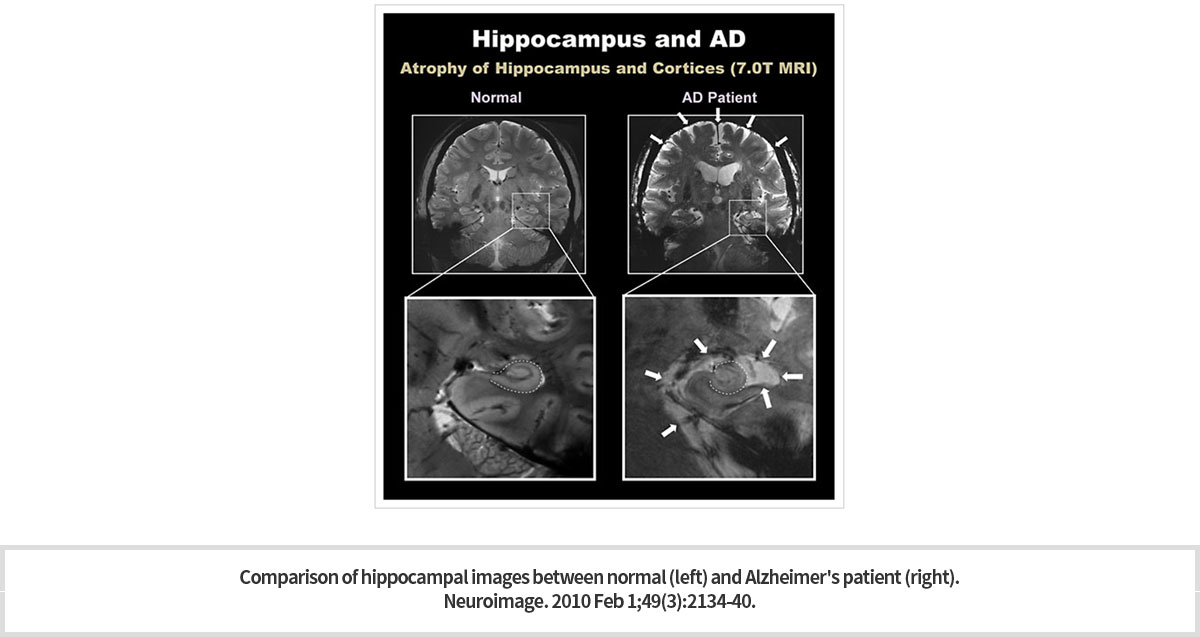
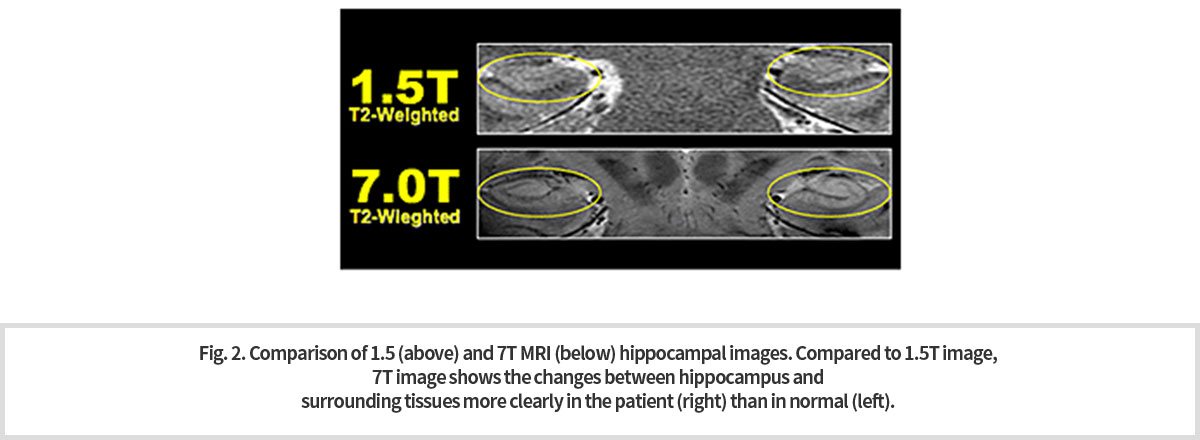
초고자장 7T MRI는 해마의 “머리와 몸”, “몸과 꼬리” 사이의 경계를 확실히 보여 주고 있다. 이와 같이 해마의 윤곽 및 구조를 파악할 수 있게 되어 해마 용적 측정이 가능하게 되었다. 7.T MRI로 획득한 선명한 3차원 영상은 해마와 관련된 질환 진단에 도움을 줄 수 있다. 7T MRI 영상을 통하여 알츠하이머 치매 환자에서의 해마의 세부 구조 및 크기가 정상인의 그것과는 극명한 차이를 보이는 것을 쉽게 관측할 수 있다 (Fig. 1).
-
Ultra-high magnetic 7T MRI clearly shows the boundary between "head and body" and "body and tail“ of hippocampus. As such, it is possible to measure the hippocampus volume as the outline and structure of the hippocampus can be identified. The clear, three-dimensional images acquired with 7.T MRI also can help diagnose hippocampal-related diseases and distinguish
the differences of the fine structure and size of hippocampus of normal subject and Alzheimer’s patient (Fig. 1).
-
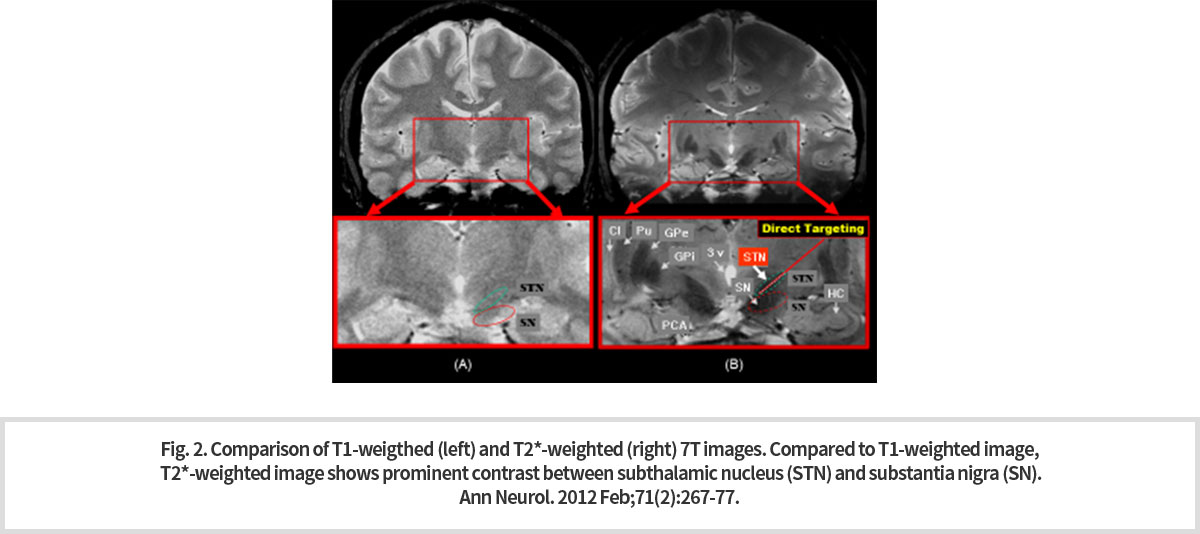
기존 1.5T 또는 3T MRI로 획득한 영상들로는 해상도가 제한적이었기 때문에 작은 용적 변화와 구조 변화 관찰은 매우 어려웠다. 특히, 뇌 심부 구조물은 영상 촬영 방식에 따라서 신호의 세기와 대조도가 다르게 나타난다. 7T 고해상도 영상 중에서 T1 강조 영상보다 T2* 강조 영상이 뇌 심부 구조물의 경계를 명확하게 보여주고 있다.
-
Because the resolution was limited with images acquired with existing 1.5T or 3T MRIs, small volume and structural changes were very difficult to observe. In particular, the intensity and contrast of signals of structures deep in the brain differ depending on the imaging method. Among the 7T high-resolution images, T2* weighted images over the T1 weighted clearly show the boundaries of the brain's deep-in structure.
-
7T MRI에 의한 3차원 T2* 강조 영상의 선명한 대조와 정확한 용적 측정법은 질병의 정확한 진단뿐만 아니라 기초 의학 연구에도 도움이 될 것이다. 특히 파킨스 질환과 같은 질병에서는 DBS 를 통한 주요한 치료 방법의 적용에 있어서 명확한 해부학적인 가이드라인을 제공할 수 있을 것으로 판단되고 있다 (Fig. 2).
-
Clear contrast and accurate volumetric methods of three-dimensional T2* weighted images by 7T MRI will help not only accurate diagnosis of disease but also basic medical research. In particular, T2* weighted images are also expected to provide clear anatomical guidelines for the treatments through DBS of the diseases such as Parkinson's disease (Fig. 2).
-
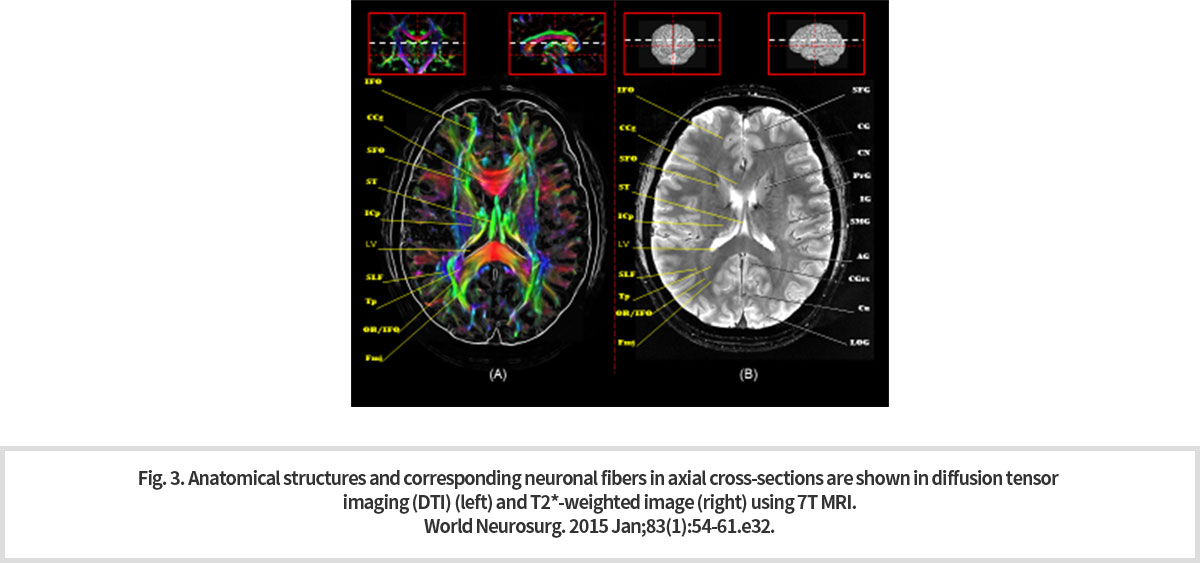
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)는 뇌 신경 다발 내 물 분자의 운동성을 계산하여 뇌 신경의 방향을 알아낼 수 있는 기법이다. 색깔에 따라서 뇌 신경의 방향을 알아내는 것이 가능하다 (빨간색: right-left, 녹색: anterior-posterior, 파란색: superior-inferior). 초고자장 7T MRI로 촬영한 DTI 영상은 해상도가 높기 때문에 미세한 뇌 신경 다발을 구분하는 것이 가능하다.(Fig. 3).
-
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a technique that can determine the direction of brain nerves by calculating the motility of water molecules in a bundle of brain nerves. Thus, it is possible to determine the direction of the brain's nerves according to the color. (Red: right-left, Green: anterior-posterior, Blue: superior-inferior). In Fig. 3, the high resolution of DTI images by ultra-high magnetic 7T MRI are shown to distinguish the minute and fine nerve bundles.
-
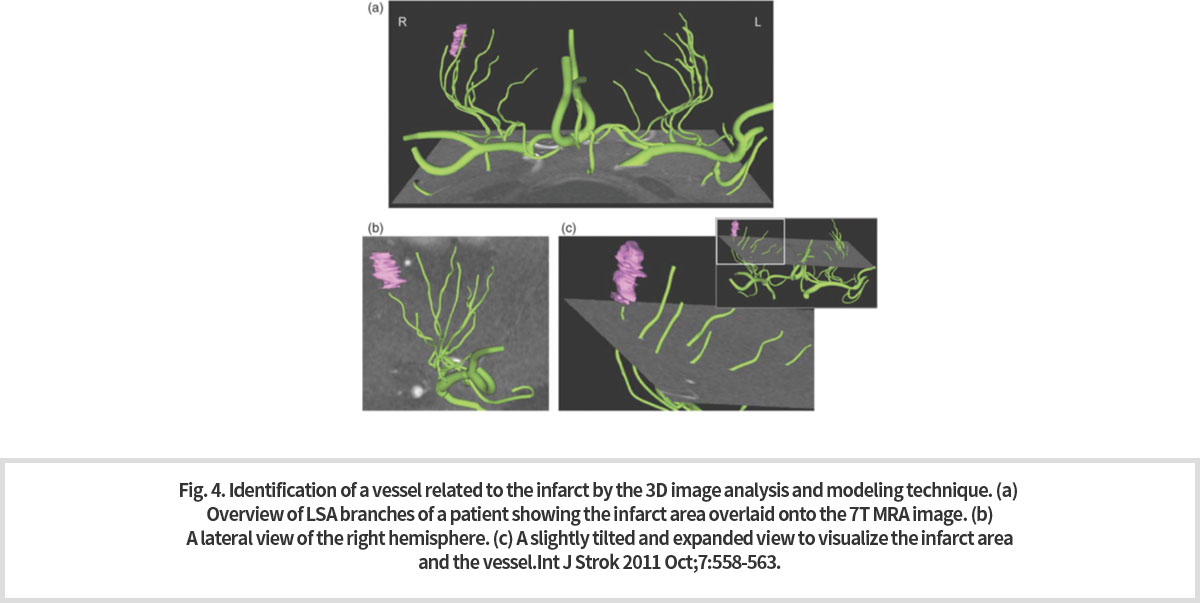
7T MRI 는 비침습적으로 미세 혈관을 촬영할 수 있는 것으로 잘 알려져 있다. 또한 높은 신호대잡음비로 인하여 고해상도의 해부학적인 영상이 가능해짐에 따라 미세 혈관의 구조적인 영상과 함께 이들 미세 혈관을 통해 혈액이 공급되는 국소 영역의 영상을 융합할 수 있게 되었다. 이를 통하여 미세한 혈관에서의 경색에 의해 직접적인 영향을 받게 될 국소 뇌 영역을 높은 정확도로 밝혀 낼 수 있는 가능성을 보여주고 있다 (Fig. 4).
-
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a technique that can determine the direction of brain nerves by calculating the motility of water molecules in a bundle of brain nerves. Thus, it is possible to determine the direction of the brain's nerves according to the color. (Red: right-left, Green: anterior-posterior, Blue: superior-inferior). In Fig. 3, the high resolution of DTI images by ultra-high magnetic 7T MRI are shown to distinguish the minute and fine nerve bundles.
2
Functional MRI: 뇌를 읽다 (Functional MRI : Reading the Brain)
-
뇌의 대사 활동은 포도당과 산소를 소모하게 되는데, 뇌활동이 발생하는 부위의 주변으로 산소를 포함한 혈류가 증가하게 된다. 이 때, MRI를 사용하여 3초 이하로 빠르게 뇌영상을 촬영하면, 혈류의 변화에 따라 신호가 변화하는 것을 영상으로 측정할 수 있다. 이러한 영상기법을 fMRI (functional MRI; 기능적 자기 공명 영상) 라고 하는데 1992년 세이지 오가와 박사 연구팀에 의해 발견되었고, 이후 뇌기능 연구의 대표적인 영상 기술로 사용되고 있다. 본 연구원은 fMRI 기법을 이용하여 기초 뇌과학 연구와 다양한 뇌질환의 임상 연구에 적용하고 있다.
-
Metabolic activity in the brain consumes glucose and oxygen. Thus, there increase the flow of blood containing oxygen in the area with high activity in the brain. It is possible to detect the signal of blood flow change (signal of oxygen content change) and make this signal into images if we catch the brain image by MRI within the short period of time such as 3 seconds. This kind of MRI technique developed by Dr. Seiji Ogawa is called fMRI (functional MRI) and has become a typical tool for research of basic and clinical neuroscience.
-
자극 기반의 뇌기능 연구
우리의 뇌는 기능에 따라 영역이 분할되어 있다. 시각, 청각, 촉각과 같은 감각 영역과 운동 영역과 같은 비교적 단순한 기능의 뇌 영역이 알려져 있다. 그러나, 인간의 인지기능, 감정기능에 대한 뇌 영역은 아직 명확하게 밝혀지지 않은 채로 남아 있다.
뇌과학자들은 이러한 뇌기능을 연구하기 위해서 연구 대상이 되는 뇌기능을 MRI 내에서 수행할 수 있도록 특정 과제(task)를 설계한다. 설계된 과제는 계획된 시간에 수행하도록 요구되며, 과제를 수행하는 동안 MRI를 이용하여 대략 2~3초 간격으로 뇌영상을 촬영하게 된다. 이렇게 획득한 MRI 뇌영상 신호는 혈류를 반영하는데, 뇌활동에 의해 뇌혈류가 증가하면, 주변 산소농도가 증가하여 MRI 신호가 증가하는 원리이다. 따라서, 과제를 수행하면서 얻은 신호 중에 특정한 타이밍에 특정 뇌 영역의 fMRI 신호가 높게 나타난다면 이는 해당 뇌 영역과 과제 기반으로 설계된 뇌기능은 서로 관련이 있음을 의미한다 (Fig. 1). -
Research of Task fMRI
Our brains has areas that are in charge of body functions. For example, there are sensory areas such as vision, hearing, and touch and motor areas. However, it is not know for the areas working for cognition and emotion.
To study the latter of the brain functions, scientists select specific tasks and take the photos of the brain by MRI for 2 ~ 3 seconds while the subject is doing the task. During doing the task, the brain shows images of areas of the increased blood flow by detecting the signal of increased oxygen contents. Owing to this kind of MRI technique, that is fMRI technique, it is possible to designate the brain area which is related to the performance of the task (Fig. 1).
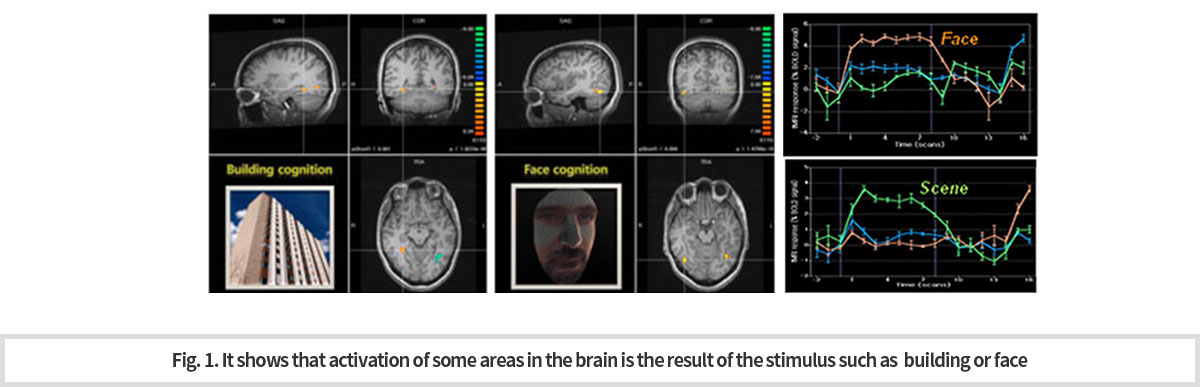
-
휴식 상태의 뇌기능 연구
뇌의 복잡한 인지과정들은 일반적으로 여러 부위의 뇌영역이 상호 연결된 일종의 네트워크로서 동작한다. 이러한 뇌의 네트워크는 특정기능을 수행하지 않는 휴식상태에서도 상호 연결되어 있으며, 서로 신경 신호를 주고 받는다는 것이 알려져 있다. 따라서, 특정 과제를 수행하지 않는 휴식상태에서 뇌영상을 촬영한 후, 영역 간 상호 상관성 분석을 통해 네트워크를 분류할 수 있다. 현재까지 알려진 뇌의 네트워크는 기본모드 네트워크(default mode network), 집행기능 네트워크(executive network), 시각 네트워크(visual network) 등이 있다. 과제 기반의 뇌기능 연구에 비하여, 검사 방법이 간단하고 빠르게 촬영할 수 있어서, 최근 임상연구에서 유용하게 활용되고 있으며, 치매, 우울증, 조현병 등 다양한 뇌질환의 임상 연구에서 유의미한 결과를 보이고 있다 (Fig. 2).
-
Resting fMRI
The complex cognition process is operated by the integrated actions of various areas of the brain which are connected by a kind of network. Even during the resting state of the brain, this net work seems to be working by serving as path for information and signal exchange among the areas. This was proved by MRI images of the resting state and the kind of network was found. So for, the basic modes of brain cognition network have been known to be three kinds which are “default mode network”, “executive network” and “visual network”. Currently, the resting fMRI is used usefully for the clinical research since compared to the task fMRI, it is rather simple in the operation. Recently, the resting fMRI has been showing the meaningful data when it is applied to various brain diseases such as dementia, depression and schizophrenia (Fig. 2).
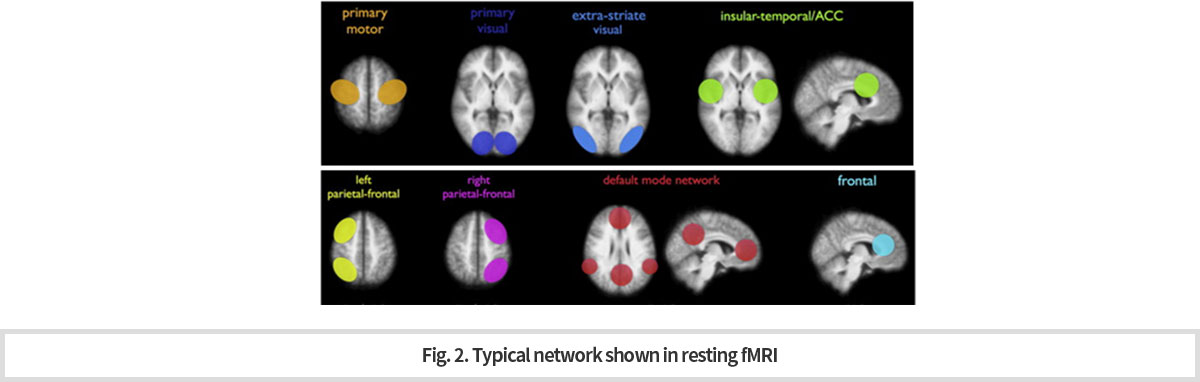
-
이러한 휴식상태 네트워크를 활용한 임상연구로서 조현병 환자군에 대한 분자 PET 뇌영상과 휴식상태 fMRI를 이용한 융복합뇌영상 (multi-modal imaging) 연구를 소개한다. 이 연구는 조현병의 도파민 가설을 기반으로 대뇌 선조체 영역 (striatal regions)과 선조체외 영역 (extrastriatal regions) 의 도파민 수용체 가용성 (availability) 분석을 시행하고, 조현병 환자군에서 도파민 수용체에 대한 [18F]fallypride 결합능(binding potential)이 유의미하게 변화된 영역을 찾은 후, 해당 영역을 seed로 하는 대뇌 기능적 연결성 변화를 확인하였다 (Fig. 3). 이는 분자 PET 뇌영상과 휴식상태 fMRI를 이용한 융복합 뇌영상 분석이 뇌질환의 정밀 진단에 유용하게 활용될 수 있음을 시사한다.
-
Recently, the resting fMRI is used together with images obtained by PET. This kind of multi-modal imaging technique is actively applied to schizophrenia. One of the multi-modal imaging studies showed that in the schizophrenic patients, there is a significant change in binding activity of dopamine receptor to [18F]Fallypride in the striatal and extrastriatal regions and then confirmed the functional change of the network connected to the areas, “as seeds”, that have the change in the binding property of the receptor (Fig. 3). This result suggests the possibility that the multi-modal imaging technique of PET and fMRI will be a useful tool for the diagnosis of various brain diseases.
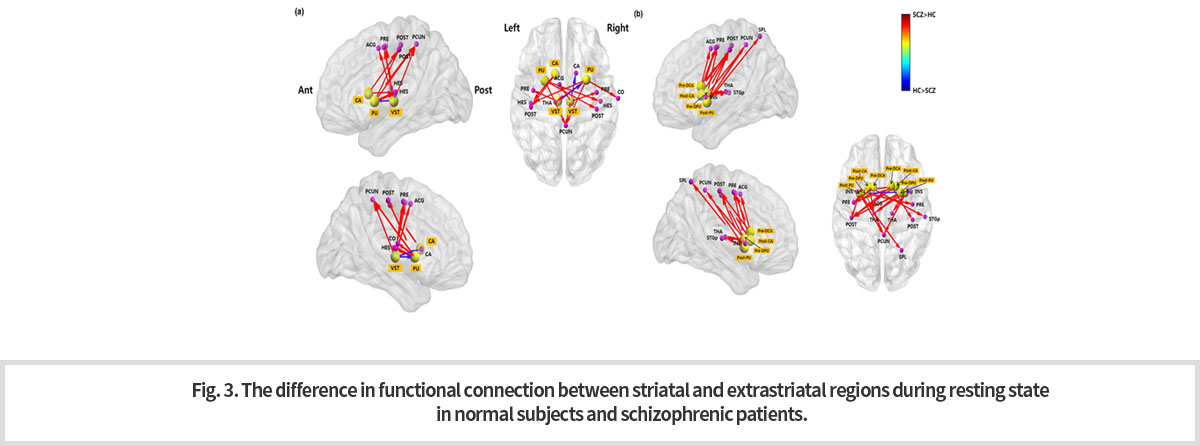
-
브레인 디코딩
최근, 인공신경망 알고리즘 및 기계학습을 이용한 자료 분석의 핵심 기술의 하나로 딥러닝(deep learning) 기술이 급격히 부상하였다. 그리고 이 기술은 많은 분야에서 활용되고 있다. 특히, 영상 인식에 있어서, 뇌에서의 기능적 네트워크의 시각 인식 처리 과정과 딥 러닝의 네트워크 기반 계층 구조에 의한 처리 과정이 유사함이 알려졌다. 이를 이용하여 특정 사물에 대한 딥 러닝 네트워크 구조 활성화 패턴과 뇌영역 네트워크 활성화 패턴을 추출하여 상관성을 분석할 수 있다. 이러한 방법에 의해서 뇌영상만으로 연구대상자가 무엇을 보고 있는지 추정하는 것이 가능해졌다. 이를 브레인 디코딩 기법이라고 한다. Fig. 4는 이 기법을 이용하여 실시간으로 측정한 뇌영상 신호로부터 실제 연구대상자가 보고 있는 영상을 추정하여 재현한 것이다.
-
Brain Decoding
Recently, deep learning technology has emerged rapidly as one of the key technologies in data analysis using artificial neural network algorithms and mechanical learning. And this technology is being used in many areas. Interestingly, in image recognition, the similarity was found between the visual recognition processing of functional networks in the brain and the processing by the network-based hierarchy of deep learning. This allows us to analyze correlation between deep learning and brain recognition for specific objects
by extracting deep-running network structure activation patterns and brain area network activation patterns. This method makes it possible to guess what the subjects are looking at with brain imaging alone. This is called brain decoding technique. Fig. 4 shows images of actual subject reproduced by this technique using images made by a real-time measurement of signals from the network of the areas involved.
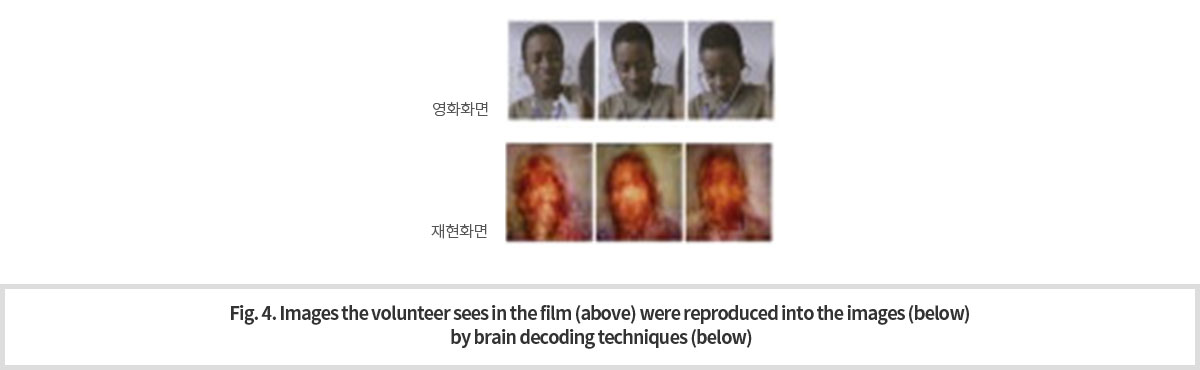
3
뇌미세혈관 미세구조 연구 및 임상응용 (Cerebral Microvascular Structure and its Applications)
-
초고자장 강도의 7T MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography) 를 이용한 뇌의 미세 혈관 영상화는 침습적인 시술 없이 생체 연구를 가능하게 하여, 뇌졸중 (중풍) 초기 단계의 미세 혈관 이상 연구에 중요한 역할을 하게 될 것으로 기대된다.
-
The microvascular imaging of the brain obtained by 7T MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography) with ultrahigh-magnetic intensity is expected to play an important role in microvascular anomaly research such as early-stage of stroke by enabling visualization of fine brain vessels without invasive procedures.
-
7T MRI는 초고장에 의하여 인체조직의 T1을 증가 시키고 T2를 감소시킴으로서 혈관 대 조직의 대조도를 높인다. 아런 유로 7T MRI는 혈관 조영시술(MRA)로의 활용이 기대된다. 천공동맥 [Lenticulostriate Artery, LSA] 의 7T MRA 영상이 기존의 침습적 혈관 조영술인 컴퓨터 조영 엑스레이 촬영법 [Digital Subtraction Angiography, DSA] 으로 촬영된 영상보다 우수한지 소뇌 AVM의 병력 (2008년 Stroke; 2009년 MRM) 이 있는 젊은 환자를 통해 조사했다. 그 결과 7T MRA 영상이 LSA를 보다 선명하고 분명하게 그려내고 있는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 또한 7T MRA에 의한 LSA영상은 1.5T MRA에 의한 영상보다도 훨씬 우수하였다 (Fig. 1).
-
7T MRI increases the contrast between blood vessels and tissues by increasing T1 and decreasing T2 of the human tissue. For this reason, 7T MRI is expected to be used for angiography (MRA). A patient with a history of lesion of cerebellum AVM (2008 Stroke; 2009 MRM) was examined to see if the 7T MRA image of Lenticulostrate Artery, (LSA] was superior to that of the existing invasive X-ray imaging angiography [Digital Subtraction Angiography, DSA]. As a result, it was observed that that the 7T MRA was drawing the image of LSA more clearly than the DSA. Also, LSA images by 7T MRA were much better than those by 1.5T MRA (Fig. 1).
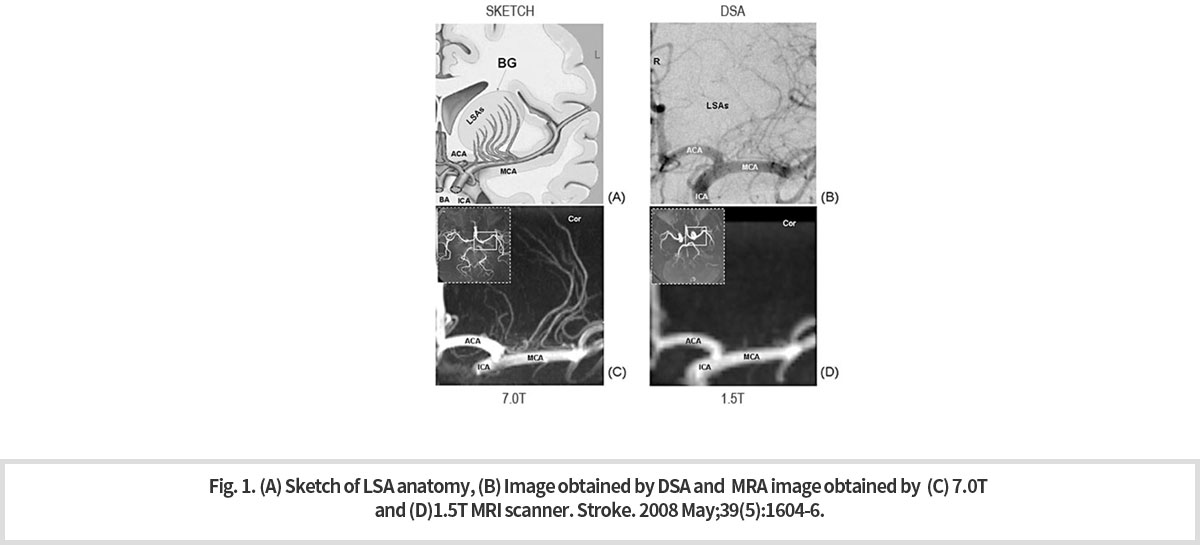
-
7T MRI가 제공하는 혈류 영상은 충분한 해상도와 신호 대 잡음비 (SNR)을 제공해 외부 자극 동안 신경 활동과 연관된 미세한 혈관의 직접적인 혈관 반응을 관찰할 수 있다. 이 같은 기능 혈류 영상(fMRA)는 특히 신경 활동 동안 혈관계 메커니즘 연구에 있어서 잠재적인 기술이 될 것이다. 화살표는 표적 혈관을 가리키며, 시각 자극이 주어진 동안 후두엽에 혈액을 공급하는 혈관이 최대 변화를 보이는 것을 확인할 수 있다 (Fig. 2).
-
The blood flow images produced by the 7T MRI provide sufficient resolution and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) to observe direct vascular reactions of fine vessels associated with nerve activity during external stimuli. These functional blood flow images (fMRAs) will be a potential technique in the study of mechanism of vascular reaction during nerve activity. The arrow points to the target vessel and we can confirm that the vessels that supply blood to the occipital lobe show a maximum change during the given visual stimuli (Fig. 2).
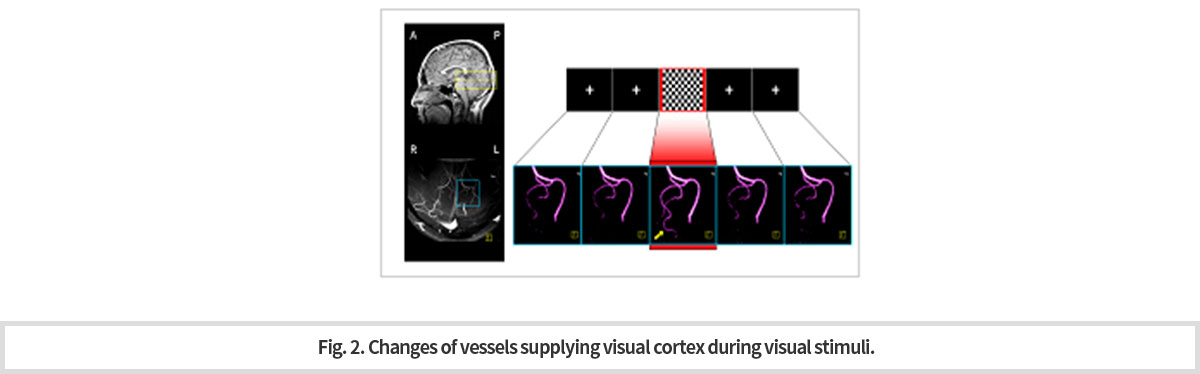
-
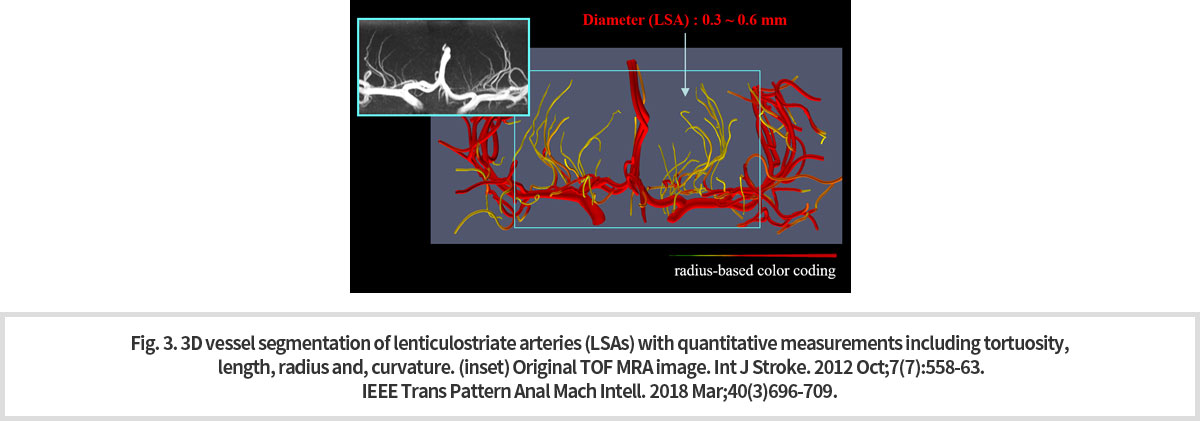
미세 혈관 분석 기법 중 3차원 혈관 분할 기술은 혈류 신호를 추적하여 혈관을 3차원적으로 분할하고 여기서 얻어진 데이터로 부터 혈관의 tortuosity, length, radius, curvature 등을 계산하여 제시할 수 있는 기술이다. 목표 혈관의 색깔을 동반한 3차원적인 시각화가 가능하며, 혈관의 정량적 특성화를 입증할 수 있는 수치를 계산하여 객관적인 정보를 제공할 수 있다. 이러한 3차원 혈관 분할 기술을 미세 혈관인 천공동맥 [Lenticulostriate Artery, LSA] 에 적용하여 3차원적인 시각화로 다음과 같이 나타냈다 (Fig. 3).
-
Among microvascular analysis techniques, the three-dimensional vessel division technique is a technique that can track blood flow signals, divide blood vessels in three dimensions, and calculate the tortuosity, length, radius, curve, etc. of blood vessels using the 3-dimensional division data. A three-dimensional visualization of the target vessel accompanied by the color is possible, and an objective information can be provided by calculating figures and thus, we can prove the quantitative characterization of the vessel. This three-dimensional vessel segmentation technique was applied to the microvessel, Lenticulostrate Artery and three-dimensional visualizations was obtained (Fig. 3).

치매-파킨슨병연구센터 연구 소개 (Research Center for Dementia & Parkinson Disease)
노 영 교수 연구 (Research of Prof. Young NOH)
1
뇌 질환 연구에 필요한 뇌 영상 해부학 기반 마련
(Establishing the basis for brain imaging anatomy necessary for the study of brain diseases)
-
초고자장 7T MRI는 해마의 “머리와 몸”, “몸과 꼬리” 사이의 경계를 확실히 보여 주고 있다. 이와 같이 해마의 윤곽 및 구조를 파악할 수 있게 되어 해마 용적 측정이 가능하게 되었다1). 7.T MRI로 획득한 선명한 3-D 영상은 해마와 관련된 질환 진단에 도움을 줄 수 있게 되었다2) (Fig. 1).
-
The ultra-high magnetic 7T MRI clearly shows the boundary between the "head and body" and "body and tail" of the hippocampus. Thus, the contour and structure of the hippocampus can be identified, enabling the size measurement of the hippocampus. Now, a clear 3-D image acquired with 7.T MRI can help diagnose hippocampus-related diseases (Fig. 1).
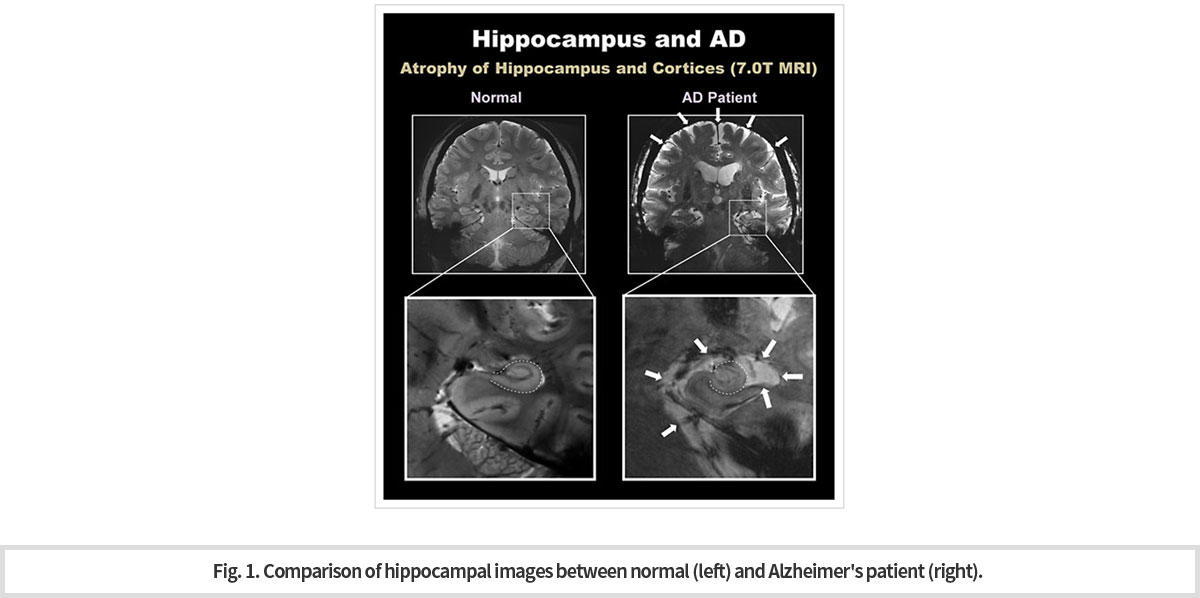
-
기존 1.5T 또는 3.0T MRI로 획득한 영상들로는 해상도가 제한적이었기 때문에 작은 용적 변화와 구조 변화 관찰은 매우 어려웠다. 7T MRI에 의한 3D T2* 영상의 선명한 대조와 정확한 용적 측정법은 질병의 정확한 진단 뿐 아니라 기초의학 연구에도 도움이 될 것이다3) (Fig. 2).
-
With conventional 1.5T or 3.0T MRI images, it is very difficult to observe small volume changes and structural changes of hippocampus because the resolution was limited. A clear contrast and accurate volumetric method of 3D T2* images by 7T MRI will be of big help to basic medical research as well as accurate diagnosis of diseases (Fig. 2).
-
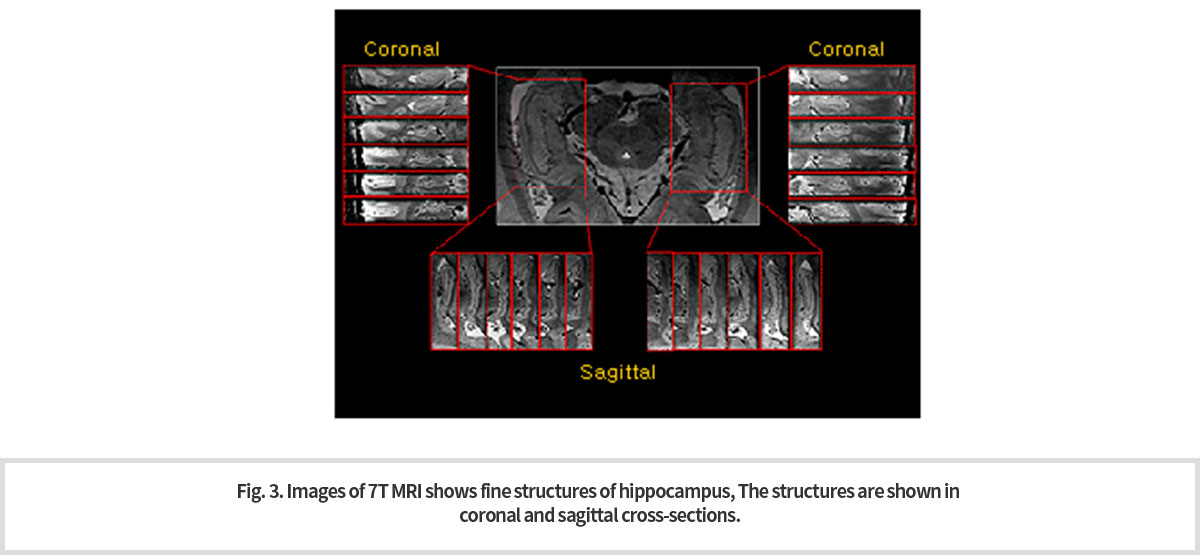
UHF 7.0T MRI의 3D 경사 에코를 사용해서 획득된 (a), (b) T2* 가중 관상 및 시상 영상은 각각의 단면에서 다양한 구조를 확인될 수 있다. 이 같은 선명한 영상으로 저자장 MRI로는 볼 수 없던 미세구조를 단면에서 관찰할 수 있게 되어 (Fig. 3) 해마와 관련이 깊은 알츠하이머병, 우울증, 정신분열병과 같은 뇌질환의 조기진단에 도움을 줄 수 있다 3).
해마 위축은 초기단계에서 미세한 부분에서 시작되나 이러한 해마의 서브필드 (subfield) 를 정확히 측정하고 정량화하는 것은 기존에 사용되고 있는 일반 해상도의 MRI로는 어렵다4). 초고자장 7.0T MRI는 알츠하이머병을 포함하여 수많은 신경계 질환을 비침습적으로 조기 진단할 수 있게 함으로써 분명 새로운 영상 의학 시대를 열 것으로 기대하고 있다. -
The T2* weighted coronary (a), and sagittal (b) images acquired by the UHF 7.0T MRI using 3D inclined echo can identify fine structures of hippocampus in each cross section (Fig. 3) . These fine images enable early diagnosis of brain diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, depression and schizophrenia.
Hippocampal atrophy begins as microscopic changes in minute subfield areas, which is very difficult to detect with the conventional MRI. The ultra-high magnetic 7T MRI is sure to open a new era of imaging medicine by enabling non-invasive early diagnosis of numerous neurological disorders including Alzheimer's disease.
-
References
1.Kim M, Wu G, Li W, Wang L, Son YD, Cho ZH, Shen D. Automatic hippocampus segmentation of 7.0 Tesla MR images by combining multiple atlases and auto-context ㅡmodels.Neuroimage. 2013 Dec;83:335-45
2. Cho ZH, Han JY, Hwang SI, Kim DS, Kim KN, Kim NB, Kim SJ, Chi JG, Park CW, Kim YB.Quantitative analysis of the hippocampus using images obtained from 7.0 T MRI. Neuroimage. 2010 Feb 1;49(3):2134-40.
3. Cho ZH, Kim YB, Han JY, Kim NB, Hwang SI, Kim SJ, Cho SJ. Altered T2* relaxation time of the hippocampus in major depressive disorder: implications of ultra-high field magnetic resonance imaging. J Psychiatr Res. 2010 Oct;44(14):881-6.
4. Cho ZH, Son YD, Kim HK, Kim ST, Lee SY, Chi JG, Park CW, Kim YB. Substructural hippocampal glucose metabolism observed on PET/MRI. J Nucl Med. 2010 Oct;51(10):1545-8.
2
파킨슨병 – 초고해상도 및 고해상도 MRI 뇌 영상을 사용한 병변의 시각화
(Visualization of brain lesion in Parkinson’s Disease)
-
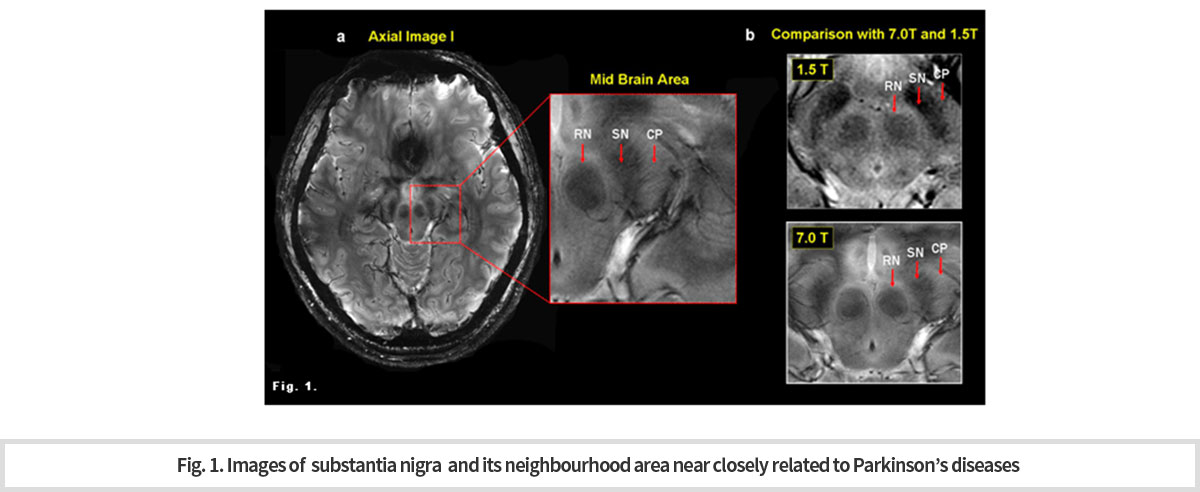
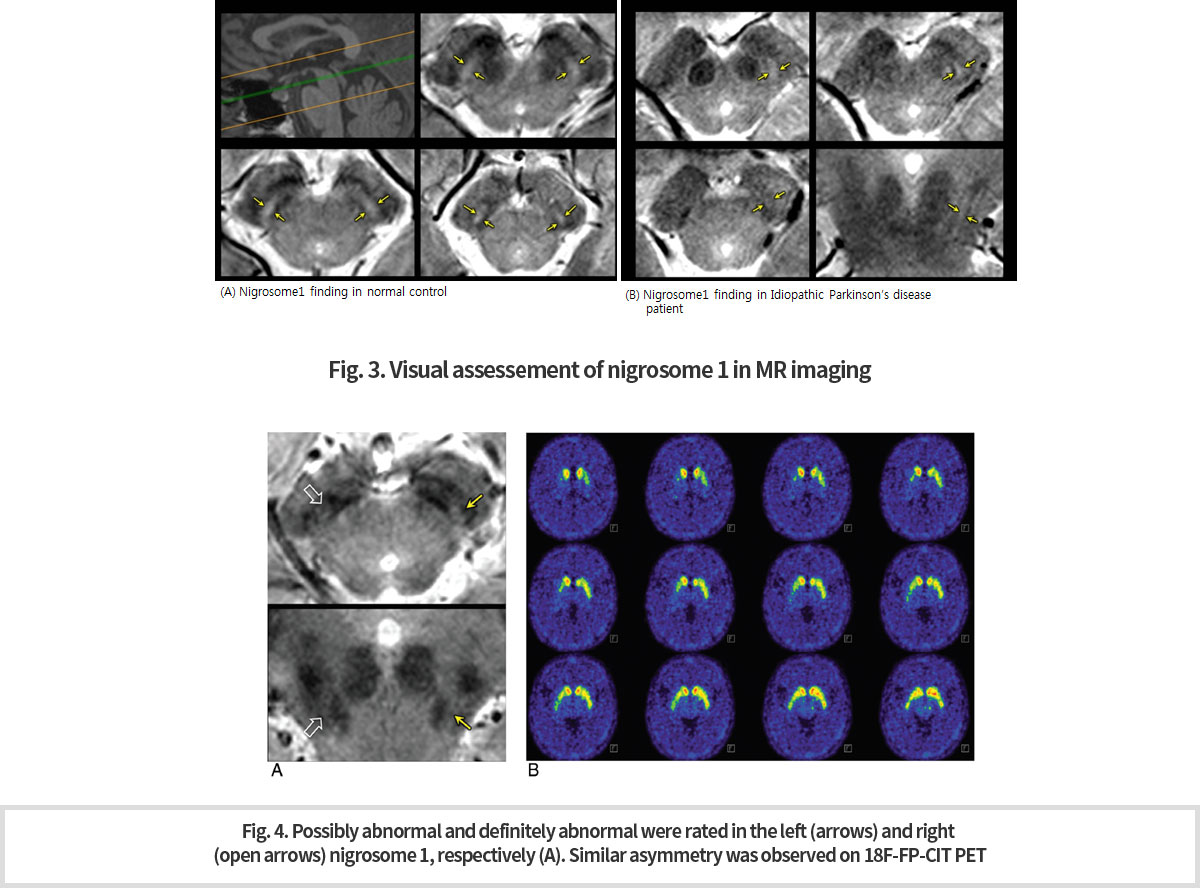
파킨슨병(PD)은 대표적인 신경변성 장애로써 흑색질(SN)에서 도파민(DA) 신경세포의 손실 진행에 의해 발생한다. 따라서 SN은 PD 진단을 위해 우리가 들여다보게 되는 가장 의심스러운 부위이다. SN에 있어서 상당량의 철 이온이 침전된다. T2* 또는 감수성 가중은 철 침전의 심대한 영향을 받으며, 이에 따라 SN과 같은 핵은 밝은 배경에 짙은 구조로 잘 나타난다(Fig. 1).
자기 감수성 효과는 정자기장의 강도와 선형으로 증가한다. 7.0T에 의한 정자장 증가는 SNR에 유의한 증가를 가져다 주며, 이로 인하여 감수성을 증가시켜 더 높은 해상도와 더 높은 대조의 영상을 획득할 수 있게 한다. 7.0T에서는 SN의 선명한 모양과 경계선 사진을 만드는 것이 가능하다 사용된 자석은 7.0T 연구 원형 MRI 스캐너(지멘스의 매그네톰 7T)이다. -
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a typical neurodegenerative disorder which is caused by the progress loss of dopamine (DA) nerve cells in the substantia nigra(SN). Therefore, the SN is the most suspicious part that we look into for PD diagnosis. A significant amount of iron ions are deposited in the SN. T2* or sensitivity increase is heavily influenced by iron precipitation and therefore nuclei such as the SN are well represented by a dark structure on a bright background.
The magnetic sensibility effect increases linearly with the strength of a static magnetic field. Increased static magnetism by 7.0T results in a significant increase in SNR, which increases sensitivity, allowing higher resolution and higher contrast images to be acquired. (Fig. 1). The magnet used is a 7.0T of MRI scanner for research (Magnetom 7T of Siemens).
-
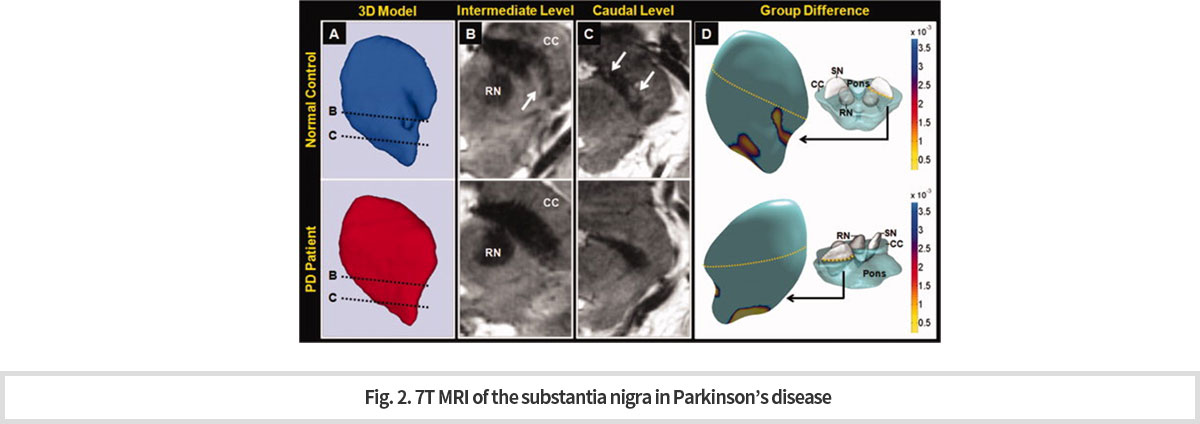
7T MRI를 환자에 적용하였다. 모든 영상은 2D T2*가중 경사 에코 연쇄를 사용해 획득한 것이다.
본 연구소에서는 이전에는 부검뇌에서만 관찰할 수 있었던 nigrosome 1 구조물을 세계 최초로 in vivo 에서 관찰할 수 있게 되었다. (Fig. 2). -
7T MRI was applied to patients. All images were acquired using a 2D T2* weighted inclined echo chain.
Our center would be the first in the world to observe the nigrosome 1 structure in vivo that was, previously only observed in the autopsy brain. (Fig. 2)
-
Nigrosome 1 구조물은 도파민 세포가 소실되는 파킨슨병 환자에서 소실된다. 이 구조물 변화의 in vivo 관찰은 파킨슨병의 영상학적 진단 바이오마커로서의 가능성을 제시하였다는데 큰 의미가 있다.
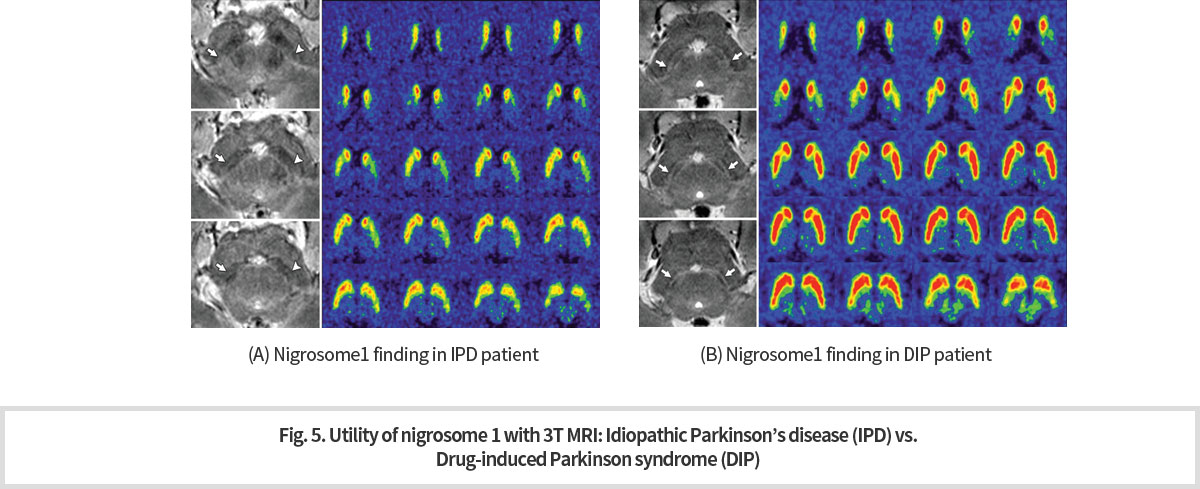
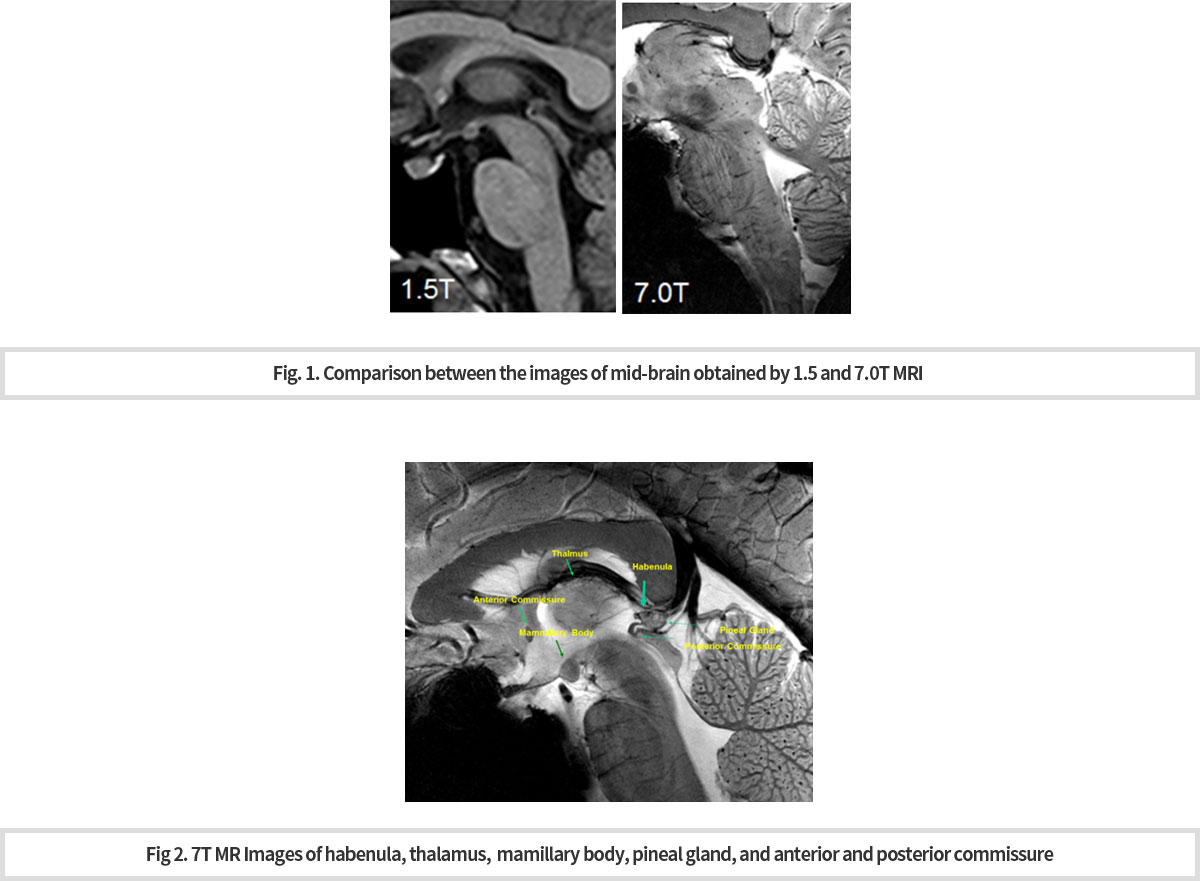
High technology 인 7T MRI 는 일반적인 임상 환경에서 사용하기에 제한 점이 있다. 따라서 우리 연구 센터에서는 7T MRI technique에서 얻은 경험을 기반으로, 범용적인 장비인 3T MRI 를 이용하여 nigorosome 1 관찰을 시도하였고 다행히 성공을 거두었다. 이 3T MRI 기법을 이용하여 정상인과 파킨슨병 환자의 nigrosome 1 구조에 차이가 있음을 확인하였으며 (Fig.3), 이 결과는 파킨슨병 진단의 골드 스탠다드로 알려진 도파민 PET 로 얻은 결과와 높은 상관 관계 있음도 관찰하였다 (Fig. 4) -
The Nigrosome 1 structure is lost in patients with Parkinson's disease where dopamine cells are lost. The in vivo observation of the change of this structure is significant in that the structural change of this organelle could be a imaging diagnostic biomarker for Parkinson's disease.
7T MRI is a high technology and thus, it has limitations for use in general clinical environments. Therefore, based on the experience gained from 7T MRI technique, our research center attempted to observe nigorosome 1 using 3T MRI, which is a universal equipment, and fortunately succeeded. Using this 3T MRI technique, we have confirmed that there are differences in the structure of nigrosome 1 between normal subjects and patients with Parkinson's disease (Fig.3). The results were also highly correlated with results obtained from dopamine PET, known as gold standard for Parkinson's disease diagnosis (Fig. 4).
-
또한 파킨슨 증상을 보이는 환자들 가운데에는 도파민 활성을 억제하는 약물로 인하여 증상을 보이는 환자들이 있다. 임상적으로 이 둘을 감별하는 것은 환자 치료 및 예후 판정에 매우 중요하다. 이 프로토콜을 통하여 파킨슨병의 진단 (Fig.3) 뿐 아니라, 약물유발형 파킨슨증후군과의 감별 진단 (Fig. 5) 이 가능 해졌다.
-
Also among patients with Parkinson's symptoms are those with symptoms caused by drugs that inhibit dopamine activity.Clinically it is critical to differentiate the drug-induce and spontaneous patients for patient care and prognosis. Through this 3T MRI protocol, not only the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease (Fig.3), but also the diagnosis of drug-induced Parkinson's syndrome (Fig. 5) became possible.
-
References
1. Cho ZH, Oh SH, Kim JM, Park SY, Kwon DH, Jeong HJ, Kim YB, Chi JG, Park CW, Huston J 3rd, Lee KH, Jeon BS. Direct visualization of Parkinson's disease by in vivo human brain imaging using 7.0T magnetic resonance imaging. Mov Disord. 2011 Mar;26(4):713-8.
2. Kwon DH, Kim JM, Oh SH, Jeong HJ, Park SY, Oh ES, Chi JG, Kim YB, Jeon BS, Cho ZH. SevenTesla magnetic resonance images of the substantia nigra in Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol. 2012 Feb;71(2):267-77.
3. Noh Y, Sung YH, Lee J, Kim EY. Nigrosome 1 Detection at 3T MRI for the Diagnosis of Early Stage Idiopathic Parkinson Disease: Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy and Agreement on Imaging Asymmetry and Clinical Laterality. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015 Nov;36(11):2010-6.
4. Sung YH, Noh Y, Lee J, Kim EY. Drug-induced Parkinsonism versus Idiopathic Parkinson Disease: Utility of Nigrosome 1 with 3-T Imaging. Radiology. 2016 Jun;279(3):849-58.
강 승걸 교수 연구 (Research of Prof. Seung-Gul KANG )
연구 주제 및 연구 방법 (Research topics and methods)
불면증, 수면장애, 우울증, 자살 등이 주요 연구대상임
The main research topics are insomnia, sleep disorders, depression, and suicide.
불면증, 자살 및 우울증은 뇌영상으로, 불면증, 수면무호흡증은 수면뇌파를 통하여 연구하고 있음.
수면장애에 대해서는 폐쇄성수면무호흡증(obstructive sleep apnea, OSA)의 정신증상과 수면뇌파를 연구하고 있고, OSA를 예측할 수 있는 방법을 연구하였음.
OSA를 머신러닝 기법으로 예측하는 연구 중에 있음.
Insomnia, suicide and depression are being studied by MRI brain images and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is by sleep EEG
(electroencephalography).
Regarding sleep disorders, psychiatric symptoms and sleep EEG of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) are investigated.
Prediction study of OSA using machine learning is ongoing.
3-1
Research on depression; discovering a image biomarker by high resolution images of 7T MRI
-
우울증 환자에서 측유상핵에 대한 7T 고해상도 뇌영상 연구와 AI를 활용한 뇌영상 바이오마커 발굴
7T MRI는 현재 사용되고 있는 1.5 또는 3.0T MRI에 비하여 높은 해상도 영상 및 signal-to-noise ratio를 주기 때문에 뇌 구조를 훨씬 잘 보여준다.(Fig. 1) 따라서 이 연구의 관심 영역인 측유상핵 (5~9mm)을 명확히 구분하고 구조변화를 확인할 수 있다. -
7T high resolution brain imaging study for habenula in depression and development of imaging biomarker using AI
7T MRI shows much better brain structure than 1.5 or 3.0T MRI currently in use because it gives high resolution images and signal-to-noise ratio.(Fig 1) Thus, 7T MRI allows us to distinguish between habenula (5 to 9 mm) and the monoamine centers and to identify the structural changes in each.
-
따라서 건강 대조군(40명), 우울증 환자 (초발, 난치성, 관해, 재발 환자 각각 20명)을 대상으로 7.0T와 3T MRI를 이용하여 habenula를 포함한 우울증 관련 뇌 영역의 영상을 얻어 분석할 예정이다. 구조적 뇌영상, resting state fMRI, diffusion tensor imaging등 여러 기법을 사용하여 분석예정이다.
-
Therefore, 7T MRI image of major depressive disorder patients and healthy control subjects will be obtained.
We will use structural brain imaging, resting state functional MRI, and diffusion tensor imaging methods to investigate the difference between depressive disorder and healthy control.
3-2
Research on depression: identifying the structural change of habenula by high resolution images of 7T MRI
-
7T MRI 영상을 이용하여 주요우울증과 대조군간의 habenula의 부피를 비교하는 중간분석을 시행하였다.
아래 Fig 3. A는 건강대조군(좌측)과 주요우울장애(우측) 환자의 7T 뇌영상으로 (a)는 MPRAGE 영상, (b)는 ME-MP2RAGE T1 map이다. 전반적으로 b의 ME-MP2RAGE T1 map의 영상이 habenula를 구분하기에 더 우수함을 볼 수 있다.
Fig 3. B는 건강대조군(우측)과 주요우울장애(좌측) 환자에서 habenula를 segmentation하여 두 군간에 부피를 비교하였다.
분석결과 주요우울장애 환자들의 우측 habenula 부피가 좌측 habenula 부피보다 작고, 건강대조군의 우측/좌측 habenula보다 작음을 확인하였다. (Fig. 4) -
Interim analysis of 7T MRI was performed to compare the volume of habenula between major depression patients and healthy control.
Fig 3. shows (a) MPRAGE and (b) ME-MP2RAGE T1 map. Overall, the contrast on the ME-MP2RAGE T1 map image is better than that on the MPRAGE image.
Fig 4. shows that smaller right habenula volume in the MDD group than the left habenula volume in the MDD group and those of the right and left habenula in HCs.
3-3
Research on insomnia; Brain reactivity to insomnia-related stimuli in insomnia patients
with subjective-objective discrepancy of sleep: task fMRI study
-
불면증의 원인과 양상은 다양하다. 불면증 중에 주관적 불면증(수면상태 오지각)은 환자 스스로는 수면을 취하지 못하였다고 하나 실제 수면시간과 상당한 차이를 보이는 불면증이다.
불면증 중 주관적-객관적 수면시간의 유의한 차이를 보이는 사람과 그렇지 않은 사람, 대조군에 대해 불면증관련 자극, 일반적 불안을 유발하는 자극, 중립적 자극을 주어 뇌활성의 변화를 비교하였다
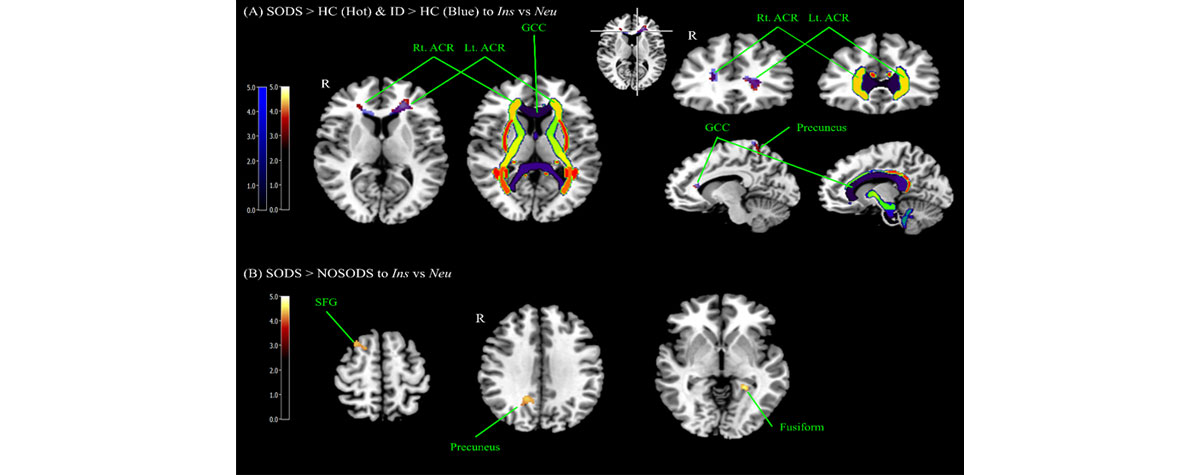
불면증 환자중 주관적-객관적 수면시간 차이를 보이는 사람(insomnia with subjective-objective discrepancy of sleep, SODS group)과 차이를 보이지 않는 사람(insomnia without subjective-objective discrepancy of sleep, NOSODS group), 대조군(healthy control, HC) 3군을 비교하였고 불면증 환자 전체와 (insomnia disorder, ID) 대조군(HC) 2군을 다시 비교하였다. 아래 Fig 5의 A그림은 주관적-객관적 수면시간 차이를 가지는 불면증 환자들이 대조군에 비해 불면증관련 자극에 대해 genu of corpus callosum, right anterior corona radiata, precuneus에서 민감한 뇌활성을 나타냄을 보여준다.
또한, 불면증 전체와 대조군 전체를 비교하였을 때에도 동일한 영역에서 증가된 뇌활성을 보였다. Fig 5의 B그림은 주관적-객관적 수면시간 차이를 가지는 불면증 환자들이 수면시간 차이를 가지지 않은 불면증 환자들에 비해 불면증 유발자극에 대해 right superior frontal gyrus, right precuneus, left fusiform에서 증가된 뇌활성을 보임을 보여준다. -
A) Brain areas showing increased BOLD signals to the contrast of Ins vs Neu among groups (SODS vs. NOSODS vs. HC; ID vs. HC). Brain areas showing increased BOLD signals in SODS and ID compared to HC group commonly included GCC and both ACR (green and yellow arrows) and precuneus to the contrast of Ins vs Neu. There was no significant areas in NOSODS compared to HC group.
B) In SODS compared to NOSODS group, right SFG, left fusiform, and right precuneus showed statistical significant to the contrast of Ins vs Neu. The statistical threshold was voxel-wise uncorrected p < 0.001 with cluster-wise FWE corrected p < 0.05 (141 voxels).
Abbreviation: SODS (insomnia with subjective-objective discrepancy of sleep group), NOSODS (insomnia without subjective-objective discrepancy of sleep group), HC (Healthy control), ID (insomnia disorder group, SODS + NOSODS), Ins (Insomnia item), Neu (Neutral item), GCC (Genu of corpus callosum), ACR (Anterior corona radiata), SFG (Superior frontal gyrus), FWE(Family-wise error).

정신의학연구센터 (Research Center for Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences)
김 종훈 교수 연구 (Research of Prof. Jong-Hoon KIM )
1
조현병에서 세로토닌 전달체 가용성과 대뇌 포도당 대사 간의 상관성 변화 검증: 다중 리간드 고해상도 PET 뇌영상 연구
(Altered Interregional Correlations Between Serotonin Transporter Availability and Cerebral Glucose Metabolism
in Schizophrenia: A High-Resolution PET Study Using [ 11 C]DASB and [ 18 F]FDG (Schizophrenia Research.
2017;182:55-65) )
-
1. 연구 배경 및 목적
- 본 연구에서는 대뇌 세로토닌 전달체 가용성(serotonin transporter availability)에 대한 [11C]DASB 분자 PET 뇌영상과 대뇌 포도당 대사(glucose metabolism)에 대한 [18F]FDG PET 뇌영상을 바탕으로 다중 리간드 PET 뇌영상(multi-tracer PET neuroimaging)을 구성함.
- 이러한 다중 리간드 PET 뇌영상을 기반으로 조현병 환자군과 정상대조군에 있어서 대뇌 전영역을 대상으로 세로토닌 전달체 가용성과 포도당 대사율 간 연결성(interregional connectivity) 분석을 수행함으로써, 조현병에서 대뇌 세로토닌 분자-포도당 대사 간 연결성(molecular-metabolic connectivity)의 병적 변화를 탐색하고자 함.
-
1. background and purpose
- In this study, we investigated brain serotonin transporter (SERT) availability and glucose metabolism using 7T MRI and high-resolution PET with [11C]DASB and [18F]FDG in antipsychotic-free patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls.
- Using this multi-tracer PET imaging, we aimed to elucidate alterations of the patterns of interregional connectivity between SERT availability and glucose metabolism in schizophrenia.
-
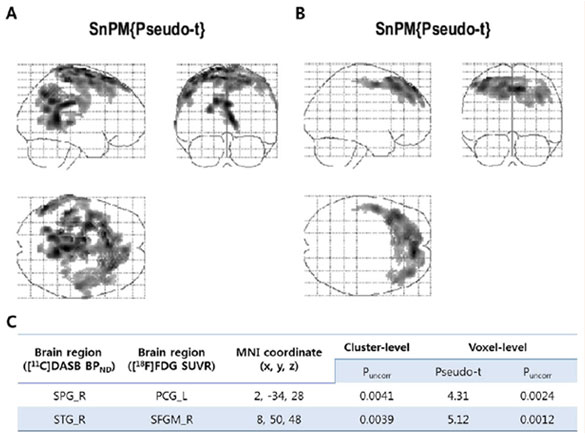
2. 세로토닌 전달체 가용성과 대뇌 포도당 대사 수준 간 상관관계 분석 :
voxel-wise permutation analysis (7500 permutations)- 조현병군과 반대로 정상대조군의 경우, 우측 상두정엽피질(right superior parietal cortex)영역의 세로토닌 전달체 가용성([11C]DASB BPND)과 좌측 후대상피질(left posterior cingulate cortex)영역의 포도당 대사([18F]FDG SUVR) 간에 유의한 양의 연결성이 관찰되었음(corrected p < 0.005).
- 또한 조현병군과 달리 정상대조군의 경우, 우측 상측두피질(right superior temporal cortex) 영역의 세로토닌 전달체 가용성([11C]DASB BPND)과 우측 전두피질(right superior frontal cortex) 영역의 포도당 대사([18F]FDG SUVR) 간에 유의한 양의 연결성이 나타났음 (corrected p < 0.005).
2. Voxel-wise permutation analysis between SERT availability
and glucose metabolism (7500 permutations)- In contrast to patients with schizophrenia, healthy subjects showed significant positive correlations between the [11C]DASB BPND of the right superior parietal cortex and the [18F]FDG SUVR of the left posterior cingulate cortex (corrected p < 0.005).
- In addition, healthy subjects had significant positive correlations
between the [11C]DASB BPND of the right superior temporal cortex and the [18F]FDG SUVR of the right superior frontal cortex (medial) (corrected p < 0.005), which were not observed in patients with schizophrenia.
-
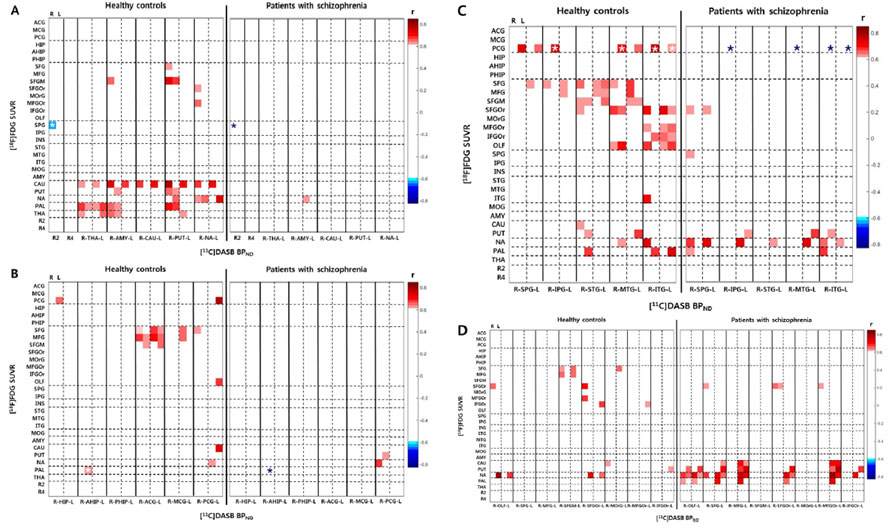
3. 세로토닌 전달체 가용성과 대뇌 포도당 대사 수준 간 상관관계 분석 :
ROI-based interregional analysis- 세로토닌 전달체 가용성과 대뇌 포도당 대사 간의 ROI 기반 상관관계 분석 결과, 조현병 환자군이 정상인에 비해 영역 간 양의 연결성(interregional positive connectivity)이 유의하게 적었음 (p < 0.01).
- 특히, 두정엽(parietal cortex)과 측두엽(temporal cortex), 후대상피질(posterior cingulate cortex) 영역 간 [11C]DASB BPND 와 [18F]FDG SUVR 간의 양의 연결성(positive connectivity)이 조현병 군에서 소실되어 있었음 (p < 0.01).
-
3. Between-group comparisons on ROI-based interregional
correlations of [11C]DASB BPND with [18F]FDG SUVR- More widespread positive correlations across the brain regions were observed in healthy subjects than in schizophrenia patients (p < 0.01). In contrast to healthy subjects, the patients with schizophrenia showed fairly limited positive interregional connectivity.
- Healthy subjects showed significant positive correlations between the SERT availability in the parietal and temporal cortices, and the glucose metabolism in the left posterior cingulate cortex,
which were absent in patients with schizophrenia (p < 0.01).
-
4. 결론
- 정상인에 비해 조현병 환자의 경우 고차원 정보처리(higher-order information processing)를 담당하는 대뇌 영역에서 세로토닌 전달체 가용성과 포도당 대사 간의 정상적인 연결성(positive connectivity)이 와해되어 있으며, 이는 조현병의 병태생리가 대뇌의 신경 연결성 장애와 밀접히 관련되어 있음을 시사함.
-
4. Conclusion
- These results suggest altered functional connectivity between the higher-order cortical regions in schizophrenia.
Our results support the notion that schizophrenia is a disorder of neuronal connectivity by demonstrating that the functional topography is disrupted in antipsychotic-free patients with schizophrenia.
- These results suggest altered functional connectivity between the higher-order cortical regions in schizophrenia.
2
청년기 우울증에서 분자 PET 뇌영상을 이용한 대사성 글루타메이트 수용체 가용성 및 기능적 연결성의 변화
(In Vivo Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Availability-Associated Functional Connectivity Alterations in
Drug-Naïve Young Adults With Major Depression (European Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019;29:278-290))
-
1. 연구 배경 및 목적
- 본 연구는 청년기 우울증군과 정상대조군에 대하여 [11C]ABP688 분자 PET 뇌영상을 이용하여 대사성 글루타메이트 수용체-5 가용성(mGluR5 availability)을 정량화 하고, 분자 PET 뇌영상에서 mGluR5 가용성에 유의한 변화가 나타난 클러스터(voxel-cluster)를 중심(seed)으로 휴지기 기능적 자기공명영상(resting-state functional MRI) 기반 기능적 연결성(functional connectivity)을 분석하는 다중 영상(multi-modality imaging) 연구임.
-
1. background and purpose
- The aim of this multimodal imaging study was to quantify in vivo mGluR5 availability using [11C]ABP688 PET in drug-naïve young adult patients with major depression as well as in matched healthy controls. To examine the functional significance of possible alterations in mGluR5 availability, we also performed resting-state functional MRI (rs-fMRI) in the same subjects, and conducted functional connectivity analyses using rs-fMRI data with regions derived from quantitative PET analysis as seeds.
-
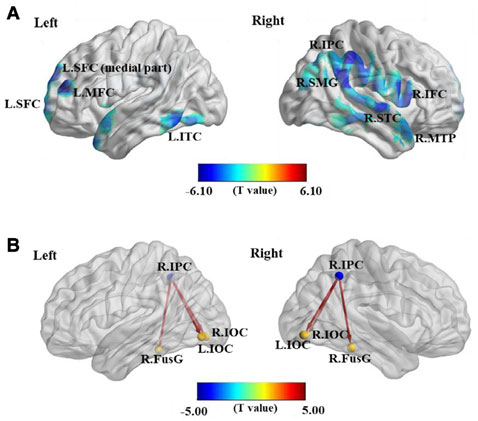
2. 대사성 글루타메이트 수용체 가용성 차이 및 기능적 연결성의 변화 분석
- (A) 우울증군에서 정상군에 비해 전전두엽 피질(prefrontal cortex)과 우측 하두정엽피질(right inferior parietal cortex) 영역 등에서 mGluR5 수용체 가용성이 유의하게 저하되어 있었음 (FDRp < 0.05)
- (B) 우울증군의 경우, 우측 하두정엽피질에서 하후두피질(Inferior occipital cortex) 및 방추이랑(fusiform gyrus) 으로의 대뇌 기능적 연결성이 정상군에 비해 유의하게 증가되어 있었음 (FDRp < 0.05)
2. Between-group comparisons of mGluR5 availability and
[11C]ABP688 BPND seed-based rs-functional connectivity- The mGluR5 availability was significantly lower in patients than in controls in voxel clusters within the prefrontal, temporal, and parietal cortices, and supramarginal gyrus (FDRp < 0.05)
- The [11C]ABP688 BPND seed-based functional connectivity analysis showed significantly increased (less negative) connectivity from the inferior parietal cortex seed to the fusiform gyrus and inferior occipital cortex in patients than in controls (FDRp < 0.05).
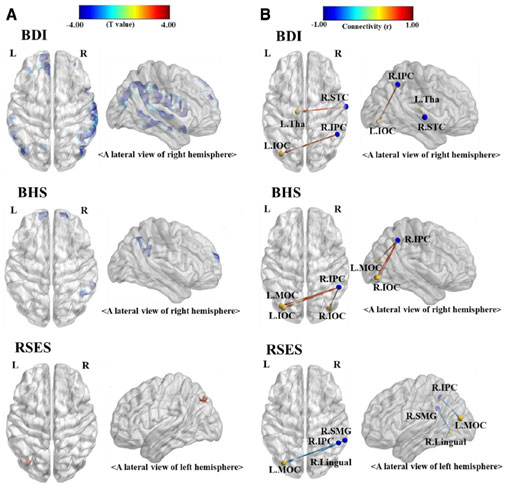
-
3. 우울증 임상변인과 mGluR5 수용체 가용성 간의 관련성 분석
- 임상변인(clinical variables)과 mGluR5 수용체 가용성 간 상관분석에서 우울감(BDI), 절망감(BHS)과 mGluR5 수용체 가용성 간에 유의한 음의 상관관계(negative correlation)가 관찰되었고(p < 0.001), 자존감(RSES)과 mGluR5 수용체 가용성 간에는 유의한 양의 상관관계(positive correlation)가 관찰되었음 (p < 0.001).
3. Correlation analysis between clinical variables and mGluR5 availability
- In the entire subject group, the BDI and BHS scores had significant negative correlations with mGluR5 availability ([11C]ABP688 BPND) (p < 0.001), whereas the RSES score had significant positive correlations with mGluR5 availability ([11C]ABP688 BPND) (p < 0.001).
-
4. mGluR5 수용체 가용성과 기능적 연결성 간의 다변량 분석
(multivariate analysis)- mGluR5 seed 클러스터와 기능적 연결성 강도(functional connectivity strength β) 간의 다변량 분석 결과, 전두피질 (superior frontal cortex) 영역의 mGluR5 가용성과 전두피질에서 해마곁이랑(parahippocampal gyrus)으로의 기능적 연결성 강도 간의 관련성이 우울증군에서는 양의 상관관계가, 정상군에서는 음의 상관관계가 관찰되어 차별적 패턴(differential pattern)이 관찰되었음 (p < 0.05)
4. Association between mGluR5 availability and related functional connectivity (multivariate analysis)
- The strength of functional connectivity (β) between the left superior frontal cortex (SFC) seed and the left parahippocampal gyrus was significantly positively associated with mGluR5 availability in the left SFC in patients (p < 0.05), but was negatively associated with it in healthy controls (p < 0.05), showing differential patterns of associations (p < 0.05).
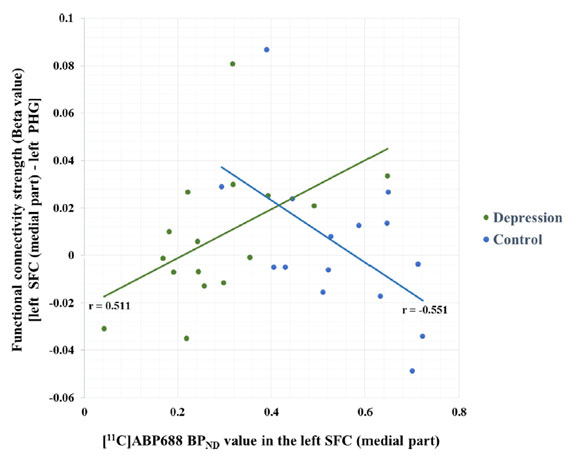
-
5. 결론
- 청년기 우울증에서 정상인에 비해 mGluR5 수용체 가용성이 저하되어 있으며, 저하된 mGluR5 수용체 가용성을 중심으로 한 기능적 연결성은 병적으로 증가되어 있음을 확인함. mGluR5 신경전달의 국소적 변화가 neural system-level에서의 기능적 연결성 변화로 파급될 수 있음을 시사함.
- mGluR5 분자 PET 뇌영상과 기능적 자기공명영상을 접목하여 분석하는 멀티모달 영상(multimodal imaging)을 이용하여 우울증의 병태생리와 관련된 새로운 in vivo biomarker를 제시함.
-
5. Conclusion
- The results suggest lower mGluR5 availability and related functional connectivity alterations in drug-naïve young adults with major depression. Our results also suggest that the foci of altered mGluR5 availability in the cortex could lead to systems-level changes in neural circuitry.
- Using a novel multimodal imaging approach combining [11C]ABP688 PET and rs-fMRI, our study provides new integrated molecular and systems-level information on the pathophysiology of depression.
3
조현병에서 고해상도 분자 PET 뇌영상을 이용한 도파민 D2/3 수용체 가용성과 정신병리와의 관련성 분석
(The Relationship Between Excitement Symptom Severity and Extrastriatal Dopamine D 2/3 Receptor
Availability in Patients With Schizophrenia: A High-Resolution PET Study With [18 F]fallypride
(Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2018;268:529-540))
-
1. 연구 배경 및 목적
- 조현병에서 도파민 신경전달물질은 병태생리학적으로 중요한 역할을 한다고 알려져 있으나, 선조체외(extrastriatal) D2/3 수용체를 매개로 한 도파민 시그널링(signaling)과 특정 정신병리학적 증상군과의 관련성은 명확히 밝혀지지 않았음.
- 본 연구에서는 [18F]fallypride 분자 PET 뇌영상을 이용해 선조체(striatum)와 선조체외(extrastriatum) 영역의 도파민 D2/3 수용체 가용성(D2/3 receptor availability)을 정량화하고 조현병의 주요 정신병리학적 증상군과의 관련성을 분석하고자 하였음.
-
1. background and purpose
- Dopamine has received much attention in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. However, the relationship between D2/3 receptor-mediated dopaminergic signaling and specific psychopathological symptom clusters is unclear.
- The aim of this study was to quantify D2/3 receptor availability in striatal and extrastriatal regions using [18F]fallypride PET and to investigate the relationship between specific psychopathological symptom clusters and D2/3 receptor availability.
-
2. 분자 PET 뇌영상 및 자기공명영상 예시
- (상) : [18F]fallypride BPND mapping 영상
- (중) : [18F]fallypride 고해상도 HRRT-PET 영상
- (하) : 3T MRI 해부학적 영상
- 분석을 위해 사용된 대뇌 관심 영역은 AAL(automated anatomical labeling) 기반으로 설정함
- PANSS 요인분석으로 얻어진 5가지 증상군(five symptom clusters)에 대한 상세 평가 시행함
2. Representative examples of [18F]fallypride PET and MR images
- (Top): [18F]fallypride BPND mapping image
- (Middle): High Resolution Research Tomography (HRRT)-PET image with 8F]fallypride
- (Bottom): 3-Tesla anatomical MRI
- The regions-of-interest (ROIs) were based on the AAL (automated anatomical labeling) atlas
- Symptoms of schizophrenia were assessed using the five-factor model of the PANSS (positive, negative, cognitive/disorganization, excitement, and depression/anxiety)
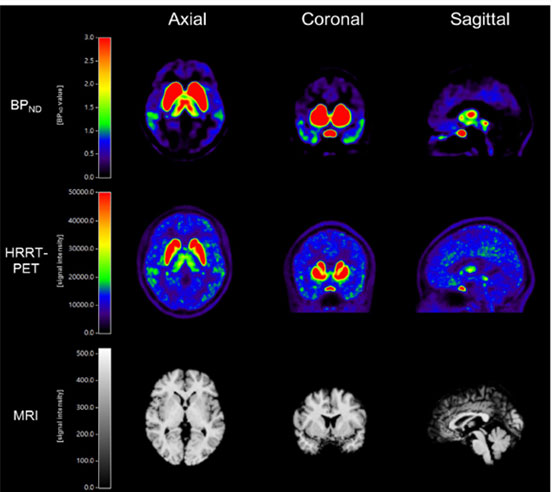
-
3. 도파민 D2/3 수용체 가용성과 정신병리학적 증상군과의 관련성
- (좌) : PANSS로 측정한 흥분증상군(excitement symptom cluster)의 심각도와 양측 대뇌섬(insula)/우측 편도핵(amygdala) 영역의 D2/3 수용체 가용성 간에 유의한 양의 상관관계가 나타남(corrected p < 0.05).
- (우) : voxel-wise 분석을 통한 대뇌 전체의 도파민 D2/3 수용체 가용성과의 회귀분석 결과에서도 우측 대뇌섬 영역의 D2/3 수용체 가용성과 흥분증상군의 심각도 간에 유의한 양의 상관관계가 확인되었음(p < 0.0001).
-
3. Relationships between psychopathology and dopamine
D2/3 receptor availability- (Left) The ROI-based analysis revealed that the severity of the excitement symptom cluster as measured by the PANSS had significant positive correlations with D2/3 receptor availability in bilateral insula and right amygdala (corrected p < 0.05)
- (Right) Voxel-wise linear regression analysis confirmed that the severity of the excitement symptom cluster had a significant positive correlation with D2/3 receptor availability in right insula (p < 0.0001)
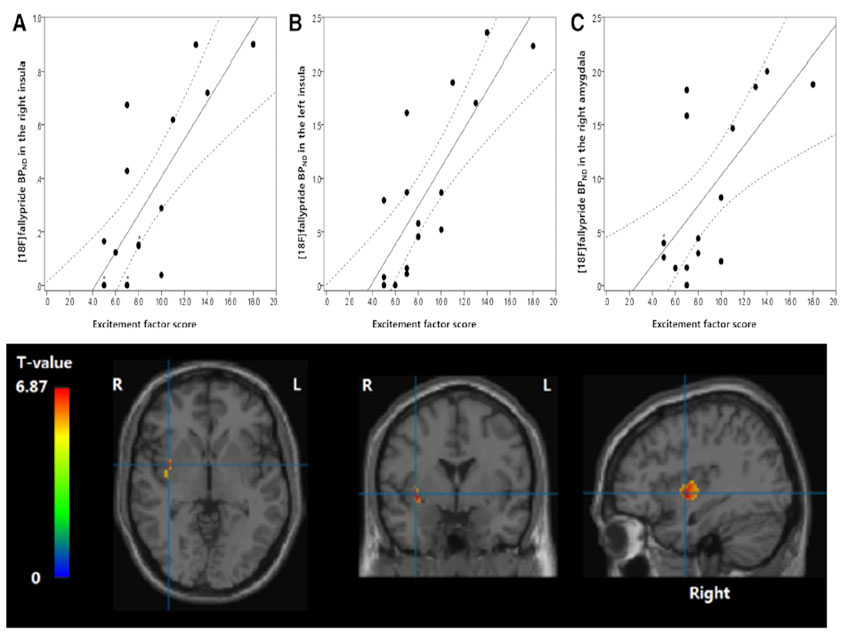
-
4. 결론
- 조현병 환자군에서 대뇌섬 영역의 도파민 D2/3 수용체를 기반으로 하는 신경전달과 정서증상 관련 정신병리 간에 유의한 양의 상관관계가 관찰되었음.
- 이는 조현병에서 관찰되는 정서증상의 병태생리에 있어 대뇌섬과 변연계를 중심으로 한 extrastriatal 도파민 시그널링이 중요한 역할을 하고 있음을 시사함.
-
4. Conclusion
- The present study revealed significant positive associations between the D2/3 receptor-mediated neurotransmission in the insula and the excitement symptom severity in schizophrenia.
- This suggests that extrastriatal dopaminergic signaling in the insula and related limbic system may play an important role in the pathophysiology of this specific symptom cluster in schizophrenia.
4
정신의학연구센터 2020년 기초연구실(BRL) 연구비 수주
(The Research Center for Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences
(Center Head: Prof. Jong-Hoon Kim) won the grant for Basic Research Lab (BRL) funded in 2020.)
-
뇌과학연구원 정신의학센터 (센터장: 김종훈 교수) 팀이 과학기술정보통신부에서 지원하는 2020년도 기초연구실 (Basic Research Lab: BRL) 사업의 연구비를 수주하였다. BRL 사업: 특정 연구주제에 대한 기초연구그룹의 융·복합 연구를 지원하여 국가 기초연구 역량 강화를 목적으로 하는 사업이다.
-
The Research Center for Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences (Center Head: Prof. Jong-Hoon KIM) won the grant for Basic Research Lab. (BRL) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) in 2020. The BRL grant aims to strengthen national research capacity by supporting advanced multidisciplinary and convergent research laboratories.
-
1. 연구기간 및 연구비
- 총 6년이며 첫 3년에 13.3억원의 연구비를 지원받으며, 3년 후 시행되는 평가를 통과하면 3년을 더 연구하게 된다.
-
1. Period and Budget of the Project
- total 6 years. W1.33 billion for the first 3 years. It can be continued for another 3 years after the evaluation at end of the first 3 years.
-
2. 연구팀
- 김종훈 교수, 손영돈 교수 (정신의학연구센터/의용생체공학과) 및 김정희 연구교수 (의공학연구센터)
-
2. Project Team
- Prof. Jong-Hoon KIM (Center Head), Prof. Young Don SON (Dept. of Biomedical Engineering, Gachon Univ. College of Health Science) and Jung Hee KIM (Medical Engineering Center, Gil Hospital)
-
3. 경쟁률
- 이번 2020년도 BRL 사업에는 총 506개 과제가 지원하였으며 이 중 12%인 61개의 연구 과제만 선정되었다.
-
3. Competition Rate
- Total 506 research teams applied to this BRL project and 61 teams (12%) won the grant.
-
4. 과제명 및 연구목적
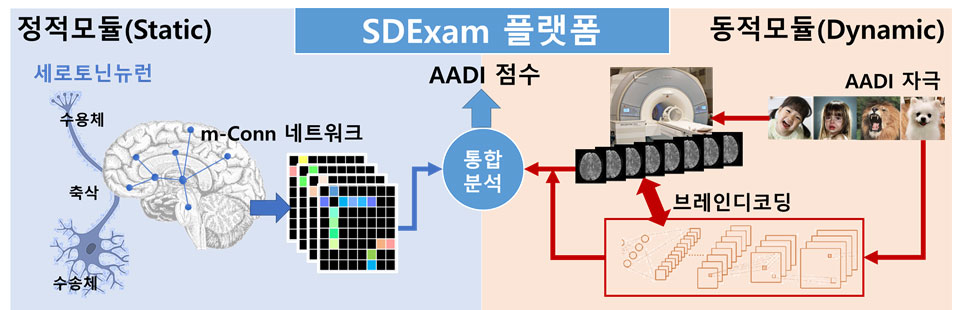
- ‘객관적 심리측정을 위한 정적/동적 뇌반응 측정 통합 플랫폼 개발’로서 본 연구에서는 사람의 심리 및 감정적 요소를 반영하는 대뇌 신경전달물질 중 하나인 세로토닌에 대한 개인별 네트워크 뇌지도를 멀티모달 영상기법을 사용하여 추출하는 정적(static) 모듈과 사람의 감정에 대해 나타나는 실시간 반응을 딥러닝 기술이 결합된 브레인 디코딩 기술로 분류하는 동적(dynamic) 모듈을 결합하여 측정하기 어려운 인간의 감정 및 심리적 요인을 뇌영상 신호로부터 객관적으로 측정할 수 있는 분석플랫폼 기술 개발을 시도할 예정이다. 본 기술은 세계 최초이며 현재의 뇌과학 기술을 한 단계 발전시킬 수 있는 핵심기술로 평가되고 있다.
-
4. Title and Aim of the Project
- As the development of the total evaluation platform for static and dynamic brain function using multimodal imaging, The project team aims to ultimately develop for the first time the core platform technology for the evaluation of human emotion and affect by combining multimodal imaging information and brain decoding technology, which is expected to significantly enhance our understanding of emotion-processing mechanisms in the human brain. To this end, the team will conduct multi-tracer molecular PET neuroimaging in combination with real-time emotional responses and functional activity measurements.

뇌척추연구센터 (Research Center for Cerebrospinal Diseases)
정태석 교수, Prof. Tae Seok JEONG
“전국 수술부위 감염 감시체계를 통해 얻은 정보분석 데이터를 통해 신경외과 영역에서의 수술부위 감염에 대한 위험요소를 찾고,
수술에 의한 감염율을 낮출 수 있을 것으로 기대되고 있다. ”
“With the analysis of information obtained through the Korean National Healthcare-Associated Infection Surveillance
System (KONIS), it is expected to find risk factors for surgical site infection in the neurosurgical field and reduce the infection
rate due to surgery.”
-
전국 수술부위감염 감시체계는 질병관리본부가 주관하는 감시체계로 국내 수술부위감염의 현 주소를 보여 줄 뿐만 아니라 이를 통하여 수술부위감염을 감소시킬 수 있는 개선책을 제시할 수 있는 중요한 프로그램이다.
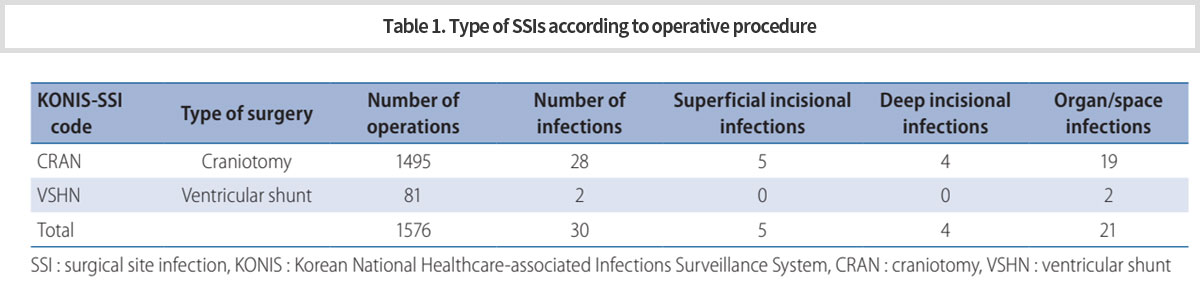
신경외과영역에서 수술부위감염에 대한 첫 전국단위 연구로서, 감염을 예방할 수 있는 수단들을 찾기 위해 수술부위감염 발생율을 분석하였다. 전체 1576사례(개두술, 1495; 뇌실복강단락술, 81)를 분석하였고, 감염율은 개두술에서 1.9%, 뇌실복강단락술에서 2.5%였다. 이 결과는 이전에 보고된 연구결과와 비슷하였다 (Table 1). -
The Korean National Healthcare-Associated Infection Surveillance System (KONIS) is operated by the Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It monitors the current status of surgical site infection (SSI) in Korea as a whole and helps develop means to reduce SSI rate. As the first study in a national survey of SSI in the neurosurgical field, we analyzed the SSI incidence to find possible means to prevent SSI.
A total of 1576 cases (craniotomy, 1495; VP-shunt, 81) were enrolled in the study. The overall SSI rate was 1.9% for craniotomy and 2.5% for VP-shunt. The results were similar to those of previously published studies (Table 1).
-
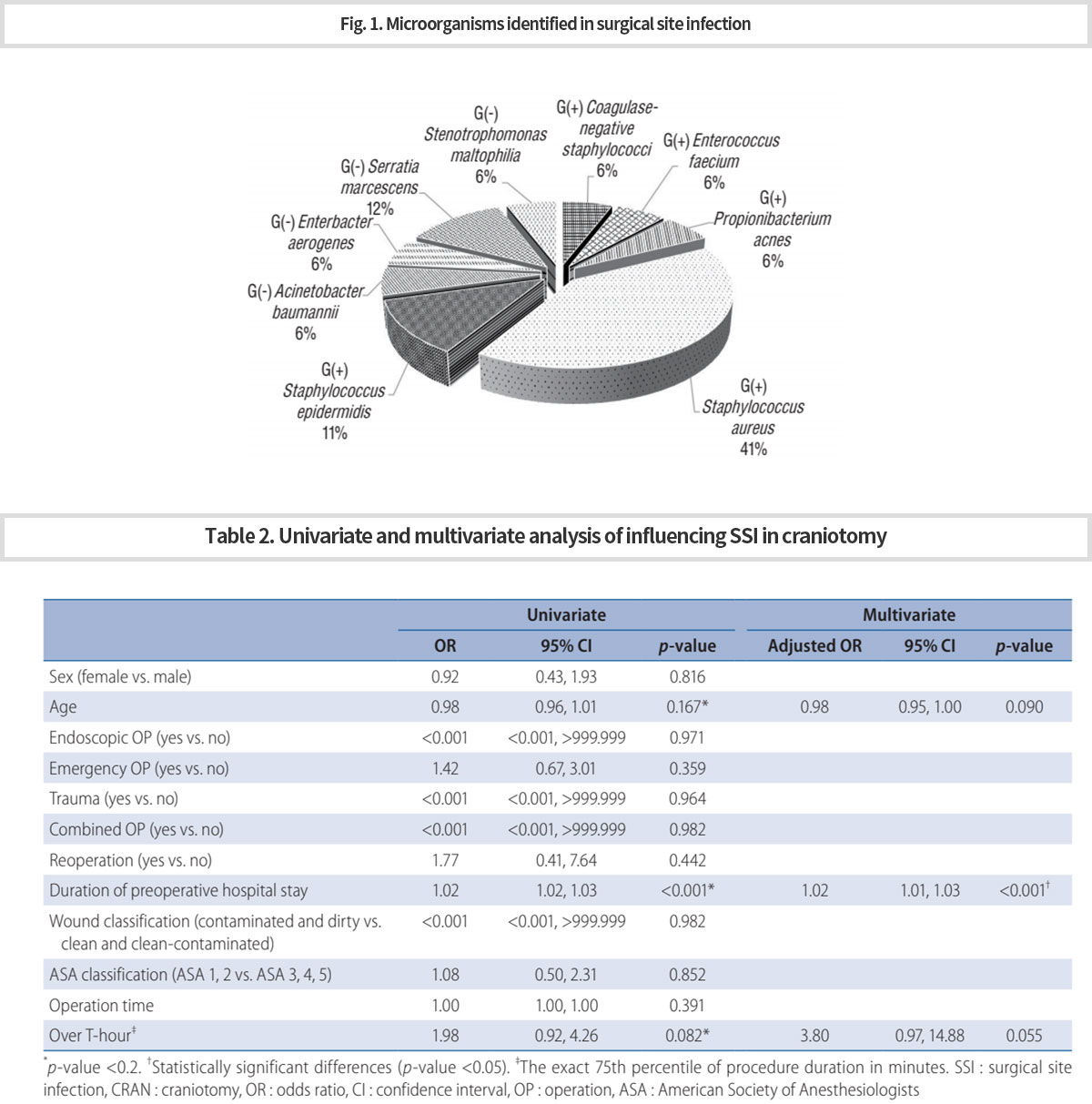
30건의 감염사례 중 기관/강 감염이 70%로 가장 많았으며, 표재성(17%), 심부(13%)감염 순이었다. 모든 세균 중 포도상구균(41%)이 가장 흔하였고, 그람음성균 중에서는 세라티아 마르세센스균(12%)이 가장 흔하였다 (Fig. 1).
수술전 재원기간이 개두술에 대한 수술부위감염의 위험요소였다. 또한 나이와 긴 수술시간이 감염위험을 높이는 경향을 보였다 (Table 2). -
Among the total of 30 infection cases, organ/space infections accounted for 70%, followed by superficial (17%) and deep (13%) infections. Staphylococcus aureus was the most common (41%) causative organism among all bacteria, and Serratia marcescens (12%) among gram-negative bacteria (Fig. 1).
Only preoperative hospital stay duration was found to be a risk factor for craniotomy. In addition, age and over T-hour tended to increase the risk of SSI (Table 2).
-
수술전 재원기간은 환자의 저하된 컨디션, 과거력, 폐렴과 같은 감염상태, 다발성외상과 같은 경우에 길어지게 되면, 이러한 상태들이 수술부위감염을 높이는 것으로 생각된다.
비록 다양한 변수들을 분석하지 못하여 수술부위감염에 대한 위험요소를 찾는데 다소 부족함이 있지만, 신경외과영역에서 수술부위감염에 대한 믿을 수 있는 결과를 보여준데 큰 의미가 있다. 향후 추가적인 데이터에 대한 분석을 통해 수술부위감염을 줄이는데 도움이 될 수 있을 것으로 생각된다. -
The duration of preoperative hospital stay is lengthened by poor general condition, histories such as diabetes mellitus and hypertension, infection status such as pneumonia, urinary tract infection, and other complications in the case of trauma. These conditions can increase the risk of SSI.
Although there is a lack of finding risk factors for SSI due to the lack of analysis of various variables, we believe that it is also very meaningful to show reliable results on the SSI rate in the neurosurgical field. In future studies, when data is accumulated, and appropriate factors are analyzed, more valuable results can be obtained to help reduce SSI incidence.


뇌대사연구센터 (Research Center for Brain Metabolism)
최 승준 교수, Prof. Seung Joon CHOI
-
본 연구 센터는 아래와 같은 연구 주제 및 사업을 수행할 예정임
- 대사와 관련된 뇌질환의 발병 기전 규명
- 대사 관련 호르몬이 뇌기능에 미치는 영향 연구
- 영양 불균형 시 신경세포의 대사와 에너지 항상 성 조절 기전 연구
- 뇌대사체 연구 추진 및 이에 필요한 기반 시설 및 연구 환경 조성
- 뇌대사 이해를 위하여 뇌대사체 측정법 개발 및 새로이 개발된 뇌대사체 측정법 실용화
- 뇌대사체 분석을 통한 뇌 질환 진단법 개발
- 뇌대사 질환의 분류 및 대사조절을 통한 치료법 개발
- 뇌대사 위험군의 선별, 모니터링 및 관리체계 확립
- 뇌대사체 연구 전문 인력 양성
- 뇌대사체 연구 활성화를 위하여 타 분야 전문가와 협력 증진 및 국내외 대학 및 연구소와 MOU 체결 추진
- 대사 관련 뇌 질환 발생에 영향을 미치는 사회적, 환경적, 유전적, 생물학적 위험요인 연구
- 위험 요인의 과학적 분석을 통한 예방법 수립
- 뇌대사 질환의 장기적 예방 전략 수립으로 국민건강 복지 증진 및 국가차원의 경제적 부담 경감에 기여.
-
The Research Center will carry out the following research topics and projects.
- Identifying the mechanism of pathogenesis of brain diseases related to metabolism
- Studying the effect of metabolic hormones on brain function
- Studying how nerve cells control the metabolism and maintain the energy homeostasis in the case of nutritional imbalance
- Promoting brain metabolite research and preparing required infrastructure and research environment
- To understand brain metabolism further, developing measurement methods of brain metabolites and settling their practical use.
- Developing brain disease diagnosis method through brain metabolite analysis
- Classifying brain metabolic diseases and developing treatment methods of these diseases through the metabolic control
- Establishing the system for screening, monitoring and management of risk group of metabolic brain diseases
- Training experts in the study of brain metabolites
- Promoting the cooperation with experts in other fields and MOUs with domestic and foreign universities and research institutes in order to promote our group’s research on brain metabolites
- Studying social, environmental, genetic and biological risk factors affecting the occurrence of metabolic brain diseases
- Establishing preventive measures of metabolic brain diseases through scientific analysis of risk factors
- Contributing to improving national health welfare and reducing the economic burden at the national level by establishing long-term prevention strategies for brain metabolic diseases.

